 PDF(1723 KB)
PDF(1723 KB)


Trust the Crowd-wisdom or AI? Research on the Impact of Human-AI Integration Fact Checking on User Information Engagement Behavior
Wu Lianren, Hu Yanan, Li Jinjie, Qi Jiayin
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2025, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (4) : 309-320.
 PDF(1723 KB)
PDF(1723 KB)
 PDF(1723 KB)
PDF(1723 KB)
Trust the Crowd-wisdom or AI? Research on the Impact of Human-AI Integration Fact Checking on User Information Engagement Behavior
[Purpose/Significance] Fact-checking is an effective strategy to combat the dissemination of misinformation. Exploring the mechanism of how fact-checking types (crowdsourced and AI fact-checking) influence users' information participation behavior can help social platforms improve and optimize their measures for misinformation governance. [Method/Process] Based on real data from social media platforms, this study used analysis of variance to investigate the impact of fact-checking on users' information participation behavior, while considering the moderating effect of source credibility. [Result/Conclusion] The empirical results show that crowdsourced fact-checking significantly affects users' information engagement behavior, with positive fact-checking promoting information participation behavior and negative fact-checking inhibiting it. AI fact-checking positively influences users' information engagement behavior, and the combination of AI and crowdsourced fact-checking also positively affects users' information engagement behavior. Source credibility positively moderates the relationship between crowdsourced fact-checking and information engagement behavior, as well as the relationship between AI fact-checking and information engagement behavior. This study reveals the impact of different types of fact-checking and their integration on information engagement behavior, providing theoretical support for social media platforms to fully utilize collective intelligence and AI for fact-checking and misinformation governance.
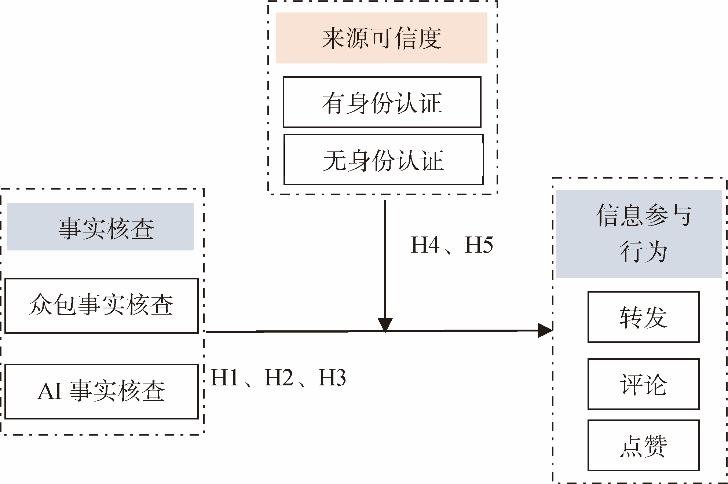
human-AI integration / crowdsourced fact-checking / AI fact-checking / information engagement behavior / source credibility
| [1] |
张新生, 王润周, 马玉龙. AIGC背景下虚假信息治理挑战、机会与策略研究 [J/OL]. 情报科学, 1-23[2025-06-22]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/22.1264.G2.20241111.1002.024.html.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
王喆诚, 于瑞峰. 社会存在、警惕性及信息卷入度对个体事实核查的影响[J]. 心理技术与应用, 2023, 11(1): 42-49.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
管佖路, 顾理平. 价值冲突与治理出路:虚假信息治理中的人工智能技术研究[J]. 新闻大学, 2022(3): 61-75, 119.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
王钰昱, 夏志杰. 基于事实核查标签的众包方法应对虚假信息的效果差异及认知机制研究[J]. 知识管理论坛, 2024, 9(3): 330-340.
|
| [28] |
李瑾颉, 聂凯伦, 吴联仁, 等. 众包事实核查对信息参与行为的影响:基于来源可信度的调节 [J]. 知识管理论坛, 2024, 9(4): 367-379.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
叶凤云, 常琳, 秦琴, 等. 基于虚假信息特征的社交媒体大学生用户感知信任研究 [J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(10): 118-127.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
吴联仁:研究选题与框架拟定,论文理论部分撰写与修改;
胡亚男:数据收集与分析;
李瑾颉:论文实证部分撰写与修改;
齐佳音:论文修改与指导。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |