 PDF(1715 KB)
PDF(1715 KB)


Evaluation Method for Highly Cited Scholars based on CNKI data
Wu Junhong, Zheng Xinyu, Sun Jun, Xiao Hong, Tang Liyun
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2025, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (3) : 232-240.
 PDF(1715 KB)
PDF(1715 KB)
 PDF(1715 KB)
PDF(1715 KB)
Evaluation Method for Highly Cited Scholars based on CNKI data
[Purpose/Significance] This study aims to measure the influence of scholars objectively and scientifically, identify a group of scholars with rich scientific research achievements and outstanding academic influence in China in the past 10 years, and guide Chinese scholars to publish more outstanding achievements in domestic journals. [Method/Process] The selection and evaluation process primarily employed bibliometric methods. For assessing individual paper impact, we utilized the Paper Citation Standardized Index (PCSI) as the evaluation metric. Author contribution weights were allocated using an optimized harmonic allocation method. The final selection of highly cited scholars was based on calculating the 'Total Author PCSI' derived from each researcher's complete publication record. [Result/Conclusion] Approximately 30,000 individuals were selected as "Top 1% Highly Cited Scholars", and around 89,000 individuals were selected as "Top 5% Highly Cited Scholars". This research achievement has achieved a comprehensive quantitative evaluation of Chinese scholars for the first time, providing a new perspective for the academic community to identify high-end talent teams, which is conducive to stimulating scholars' continuous innovation and encouraging the return of excellent domestic scientific research achievements. The selection results show that in terms of disciplinary distribution, applied economics, education, business administration, public management, and agricultural and forestry economic management have the highest number of highly cited scholars selected in the fields of humanities and social sciences. In the field of technology, disciplines such as clinical medicine, traditional Chinese medicine, electrical engineering, nursing, and civil engineering have the highest number of highly cited scholars selected. In terms of regional distribution, the regions with the highest number of highly cited scholars are Beijing, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Guangdong, and Hubei, which are developed in education and scientific research. In terms of institutional distribution, Tsinghua University, Peking University, Wuhan University, Renmin University of China and Beijing Normal University are the five institutions with the largest number of selected scholars.
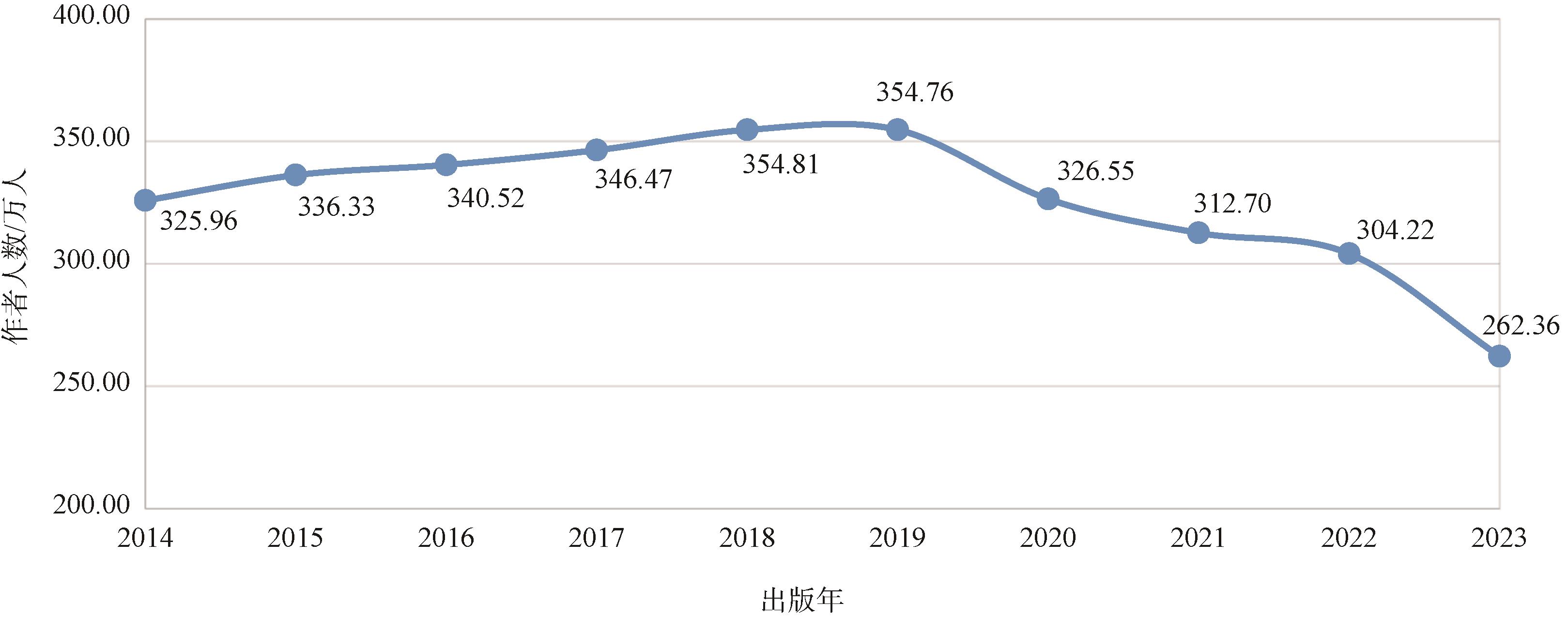
highly cited scholars / author's total PCSI / PCSI / talent evaluation / scholar evaluation
| [1] |
中共中央办公厅, 国务院办公厅.关于分类推进人才评价机制改革的指导意见[EB/OL].[2025-06-27].
General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, General Office of the State Council. Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Reform of Talent Evaluation Mechanism by Classification [EB/OL]. [2025-06-27].
|
| [2] |
中共中央办公厅, 国务院办公厅.关于深化项目评审、人才评价、机构评估改革的意见[EB/OL]. [2025-06-27].
General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, General Office of the State Council. Opinions on Deepening the Reform of Project Evaluation, Talent Evaluation and Institution Assessment [EB/OL]. [2025-06-27].
|
| [3] |
贾佳, 潘云涛, 马峥.中国高被引科学家基本特征研究——以2014汤森路透高被引科学家为例[J].科技与出版, 2014(12): 149-151.
|
| [4] |
褚农农, 乌云其其格, 姜桂兴.中国大陆高被引科学家群体状况研究[J]. 全球科技经济瞭望, 2015, 30(12): 7-13.
|
| [5] |
吴琪.从汤森路透全球“高被引科学家”名单论我国高校科研发展[J].燕山大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2015, 16(2): 132-135.
|
| [6] |
赵兵, 郭才正, 钱景.基于Clarivate Analytics “Highly Cited Researchers”的中美高被引科学家分析[J].农业图书情报学刊, 2017, 29(7): 75-77.
|
| [7] |
尹志欣, 谢荣艳.我国顶尖科技人才现状及特征研究——以汤森路透2015高被引科学家为例[J].科技进步与对策, 2017, 34(1): 136-140.
|
| [8] |
靳军宝, 曲建升, 吴新年, 等.2014—2019年我国高被引科学家群体特征计量分析[J].科技管理研究, 2021, 41(3): 202-210.
|
| [9] |
刘蓓蕾, 袁润.浅析Clarivate Analytics中国内地高被引科学家分布与科技和经济发展的关联[J].中国集体经济, 2021(4): 78-81.
|
| [10] |
赵宁, 范巍, 张锐昕.中国“全球高被引科学家”结构特征和成长规律分析——基于2014—2020年“全球高被引科学家”榜单数据[J].科技管理研究, 2022, 42(1): 208-214.
|
| [11] |
尹志欣, 由雷.从高被引科学家看中国顶尖科学人才现状及发展[J].全球科技经济瞭望, 2024, 39(5): 36-45.
|
| [12] |
魏向阳.“双一流”背景下地方高校高层次人才引进与长效机制的构建[J].河南教育学院学报(哲学社会科学版), 2019, 38(4): 94-97.
|
| [13] |
姜凡. “双一流”背景下地方高校高层次人才引育研究——基于地方高校高被引学者群体的实证分析[J].教育评论, 2021(7): 86-91.
|
| [14] |
刘俊婉.高被引科学家论文产出力的计量分析[J].情报杂志, 2013, 32(10): 67-71.
|
| [15] |
赵鑫, 朱佳妮. “高被引学者”现象研究的知识立场及其热点演变[J].上海交通大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2024, 32(8): 108-121.
|
| [16] |
Q/CNKI PJ04—2010 《中国学术期刊影响因子年报(人文社会科学)》系列标准 [S].北京:中国学术期刊(光盘版)电子杂志社, 2010.
Q/CNKI PJ04—2010.Annual Report for Chinese Academic Journal Impact Factors(Social Science) Series Standards [S]. Beijing: China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House Co., Ltd, 2010.
|
| [17] |
Q/CNKI PJ01.1—2009 《中国学术期刊影响因子年报(自然科学与工程技术)》系列标准 [S].北京:中国学术期刊(光盘版)电子杂志社, 2009.
Q/CNKI PJ01.1—2009 Annual Report for Chinese Academic Journal Impact Factors (Natural Sciences and Engineering Technology) Series Standards [S]. Beijing: China Academic Journals (CD Edition) Electronic Publishing House Co., Ltd, 2009.
|
| [18] |
伍军红, 肖宏, 任美亚, 等.PCSI:一种单篇论文被引频次标准化方法[J].图书情报工作, 2020, 64(23): 22-30.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |