 PDF(2461 KB)
PDF(2461 KB)


Research on the Health Information Interaction Behavior of Young Social Media Users: Qualitative Analysis Based on Personal Experiential Task Experiments and Behavioral Event Interviews
Li Zhifang, Shi Ziqing
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2025, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (2) : 157-175.
 PDF(2461 KB)
PDF(2461 KB)
 PDF(2461 KB)
PDF(2461 KB)
Research on the Health Information Interaction Behavior of Young Social Media Users: Qualitative Analysis Based on Personal Experiential Task Experiments and Behavioral Event Interviews
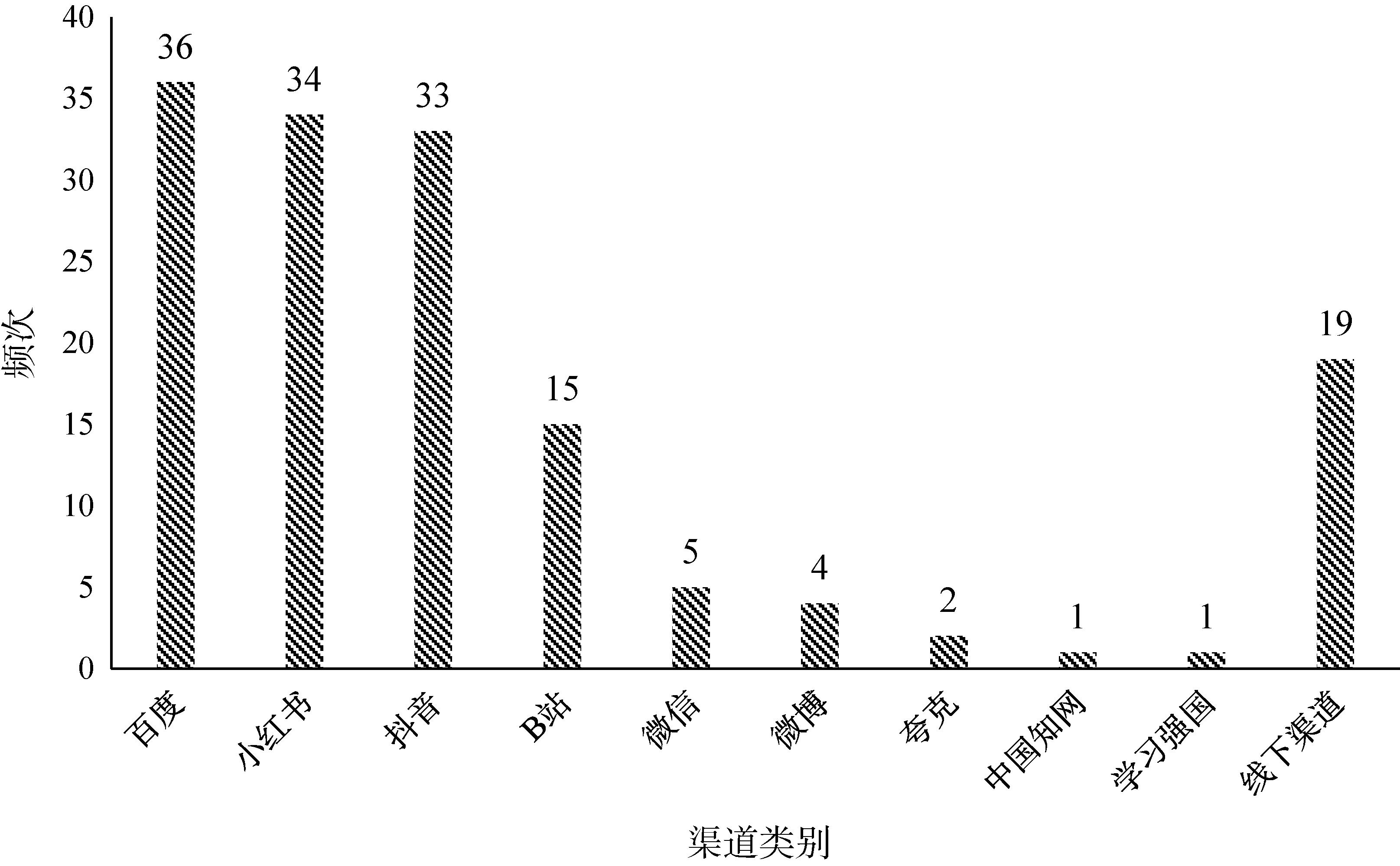
[Purpose/Significance] To explore the characteristics and inherent rules of health information interaction behavior among young social media users, and provide measures and solutions for social media intervention in users' positive health behavior. [Method/Process] In this paper, by collecting interview data, log files, experimental video data and Xiaohongshu note data, and adopting the data analysis methods of grounded theory and text mining, an in-depth analysis was conducted on the characteristics of young social media users' health information acquisition behaviors, the logic of health information quality evaluation, and the patterns of health information retrieval behaviors. And based on Engeström's Activity Theory and Kuhlthau's Information Search Process Model, an activity model of the health information retrieval behavior patterns of young social media users was constructed. [Result/Conclusion] The following conclusions were drawn: The sources from which young social media users obtain health information exhibit the characteristics of diversified choices that are mainstream-oriented and demand-driven. The ways in which they pay attention to health information content are mostly demand-based retrievals triggered by recommendations, and the categories of attention fall into multiple core areas of concern. Young social media users' evaluation paths for health information quality follow a dual path of subjective cognition and objective perception. The basis for judging the trustworthiness of health information is a collaborative inspection-style information assessment through the convergence of content and the consensus of comments, and the evaluation method of health information is based on the principle of the minority obeying the majority.
health information / interaction behavior / social media users / activity theory
| 1 |
国家卫生健康委员会.2024年中国居民健康素养监测情况[EB/OL]. [2025-04-24]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/cms-search/downFiles/06ae65a7f6644a6aa9e11a37c83095f7.pdf.
(National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Monitoring of health literacy of Chinese residents in 2024[EB/OL]. [2025-04-24]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/cms-search/downFiles/06ae65a7f6644a6aa9e11a37c83095f7.pdf.)
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
宗慧源, 赵宇翔, 宋士杰.内容社交平台赋能用户日常健康信息获取行为——基于App漫游法和关键事件技术法的质性分析[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(12): 54-62.
|
| 4 |
薛翔, 马海云, 赵宇翔, 等.失真健康信息情境下社交媒体用户分享前验证意向影响因素研究[J/OL]. 情报资料工作[2025-02-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1448.G3.20241204.0955.002.html.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
宋士杰, 赵宇翔, 宋小康, 等.互联网环境下失真健康信息可信度判断的影响因素研究[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2019, 45(4): 72-85.
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
毛太田, 马家伟, 吴鑫, 等.移动社交媒体健康信息规避行为用户画像实证研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2023, 67(10): 116-127.
|
| 9 |
方洁, 杨轶涵, 王斐.健康信息偶遇情境下高血压患者信息共享意愿影响因素研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2024, 45(4): 76-86.
|
| 10 |
高春玲, 姜莉媛, 董天宇.基于BERTopic模型的老年人健康信息需求主题演化研究——以新浪微博平台为例[J]. 情报科学, 2024, 42(4): 111-118.
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
张秀, 李月琳.年龄梯度视角下网络用户健康信息甄别能力研究[J]. 情报学报, 2019, 38(8): 838-848.
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
孙丽, 王宇婷, 曹锦丹.任务类型对用户网络健康信息搜寻行为的影响研究[J]. 情报科学, 2015, 33(9): 131-135.
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
曾粤亮, 张莉莉, 吕晓龙, 等.信息生态理论视角下大学生网络健康信息焦虑形成影响因素与对策研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2024, 68(1): 137-150.
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
周晓英, 张璐.基于活动理论的非线性信息搜寻行为模型研究[J]. 图书情报知识, 2018(1): 4-15.
|
| 27 |
薛翔, 赵宇翔, 马海云, 等.活动理论视角下的信息偶遇行为模型研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2021, 44(9): 97-105.
|
| 28 |
董洪哲, 宋小康, 赵宇翔.基于活动理论的在线健康信息替代搜寻行为模型研究[J]. 现代情报, 2023, 43(10): 54-63.
|
| 29 |
|
李志芳:提出研究问题,撰写与修改论文;
石紫晴:采集和处理数据,修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |