 PDF(3142 KB)
PDF(3142 KB)


Research on the emotional theme of public emergencies from the perspective of netizen psychology
Zheng Xingran, Huang Weidong
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2024, Vol. 9 ›› Issue (1) : 93-107.
 PDF(3142 KB)
PDF(3142 KB)
 PDF(3142 KB)
PDF(3142 KB)
Research on the emotional theme of public emergencies from the perspective of netizen psychology
[Purpose/Significance] The psychological theory of netizens is introduced to study the of emotional theme and explore the psychological causes of the outbreak of netizens' emotions and the triggering and generation of negative public opinion phenomena in public emergencies, so as to provide help for the guidance of public opinion in public emergencies. [Method/Process] Taking "China Eastern Airlines crash" as the keyword to crawl Weibo comments as the research object, using sentiment analysis, LDA theme mining, combined with public opinion life cycle and social network methods, the themes that users are concerned about under different emotions at different stages of the incident were visually analyzed. And combining with netizens' psychology, a more in-depth excavation of emotional themes in online public opinion were carried out to find out the psychological problems behind the formation of negative emotions of netizens and the behaviors that lead to negative public opinion. [Result/Conclusion] The study shows that in addition to the factors of the incident itself, the causes of negative behaviours of netizens are catalyzed by the individual psychology and group psychology of netizens as well as their potential psychological activities. The research results can help alleviate the risk of public opinion crisis and effectively guide the direction of public opinion.
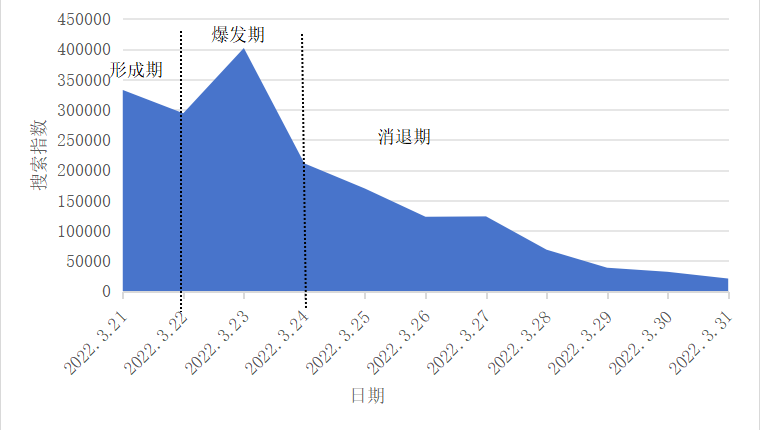
Deep learning / Emergencies / Emotional themes / Public opinion guidance / Psychology of netizens
| [1] |
徐晓日,刘丹琳.我国突发公共事件舆情治理研究的热点主题与演进趋势[J].行政与法,2023(6):15-27.(XU X R, LIU D L. Hot topics and evolutionary trends of research on the governance of public opinion on public emergencies in China[J]. Administration and law, 2023(6):15-27.)
|
| [2] |
刘勇,王雅琪.公共危机中“次生舆情”的生成与演化——基于对“8·12天津港爆炸事故”的考察[J]. 国际新闻界,2017,39(9):116-133.(LIU Y ,WANG Y Q. The generating and evolution of "Secondary Public Sentiment" in public crisis: based on the focus on “8·12 Tianjin Port Explosion”[J]. Chinese journal of journalism & communication,2017,39(9):116-133.)
|
| [3] |
王平,谢耘耕.突发公共事件网络舆情的形成及演变机制研究[J].现代传播(中国传媒大学学报),2013(3):63-69.(WANG P, XIE J Y. Research on the formation and evolution mechanism of network public opinion in sudden public events[J]. Modern Communication(Journal of Communication University of China),2013(3):63-69.)
|
| [4] |
吕鲲,施涵一,靖继鹏.突发公共卫生事件网络舆情热点话题形成组态路径研究——基于微博热搜数据的模糊集定性比较分析[J].情报理论与实践,2022,45(9):148-156.(LÜ K, SHI H Y, JING J P. Research on the configuration path of online public opinion hot topics in public health emergencies: fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis based on microblogging hot search data[J].Information studies: theory & application,2022,45(9):148-156.)
|
| [5] |
CHEN T, PENG L, YANG J, et al. Modeling, simulation, and case analysis of COVI D‐19 over network public opinion formation with individual internal factors and external information characteristics[J]. Concurrency and computation: practice and experience, 2021: e6201.
|
| [6] |
杜洪涛,王君泽,李婕.基于多案例的突发事件网络舆情演化模式研究[J].情报学报,2017,36(10):1038-1049.(DU H T, WANG J Z, LI J. Research on evolution model for online public opinion of emergent events based on multiple cases[J].Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information,2017,36(10):1038-1049.)
|
| [7] |
宋海龙,巨乃岐,张备,等.突发事件网络舆情的形成、演化与控制[J].河南工程学院学报(社会科学版),2010,25(4):12-16.(SONG H L, JU N Q, ZHANG B, et al. Formation, evolution and control of network public opinion for emergencies[J].Journal of Henan University of Engineering(social science edition), 2010,25(4):12-16.)
|
| [8] |
佘廉,叶金珠.网络突发事件蔓延及其危险性评估[J].工程研究-跨学科视野中的工程,2011,3(2):157-163.(SHE L, YE J Z. The Assessment on internet emergency spread and its risk[J].Journal of engineering studies, 2011,3(2):157-163.)
|
| [9] |
任中杰,张鹏,李思成,等.基于微博数据挖掘的突发事件情感态势演化分析——以天津8·12事故为例[J].情报杂志,2019,38(2):140-148.(RENG Z J, ZHANG P, LI S C, et al. Analysis of emotion evolution of emergencies based on Weibo data mining: taking "8·12 Accident in Tianjin" as an example[J].Journal of intelligence,2019,38(2):140-148.)
|
| [10] |
ALMARS A, LI X, ZHAO X. Modelling user attitudes using hierarchical sentiment-topic model [J]. Data & knowledge engineering, 2019,119: 139-149.
|
| [11] |
姚艾昕,马捷,林英,等.重大突发公共卫生事件谣言演化与治理策略研究[J].情报科学,2020,38(7):22-29.(YAO A X, MA J, LIN Y, et al. The rumor evolution and governance strategy of major public health emergencies[J].Information science,2020,38(7):22-29.)
|
| [12] |
WANG S, LI L, YANG C, et al. Regularized topic-aware latent influence propagation in dynamic relational networks [J]. GeoInformatica, 2019, 23(3):329-352.
|
| [13] |
SCHOENMUELLER V , BLANCHARD S J , JOHAR G V . Who will share fake-news on Twitter?
|
|
psycholinguistic cues in online post histories discriminate between actors in the misinformation ecosystem[J].Computers and society, 2022,39(2):11-18.
|
| [14] |
王英杰,胡漠,张津赫,等.信息疫情下短视频网络舆情预警指标体系构建研究[J].情报科学,2021,39(11):38-44.(WANG Y J, HU M, ZHANG J H. Early warning index system of short video network public opinion under infodemic[J].Information science,2021,39(11):38-44.)
|
| [15] |
李玥琪,王晰巍,王楠阿雪,等.突发事件下社交媒体网络舆情风险识别及预警模型研究[J].情报学报,2022,41(10):1085-1099.(LI Y Q, WANG X W, WANG N A X, et al. Risk identification and early warning model of social media network public opinion in emergencies[J].Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information,2022,41(10):1085-1099.)
|
| [16] |
PENG L J, SHAO X G, HUANG W M. Research on the early-warning model of network public opinion of major emergencies[J]. IEEE access,2021,9:44162-44172.
|
| [17] |
马宁,于光,闫相斌.基于舆情评论数据挖掘的政府回应策略优化方法研究——以新冠疫情援助物资使用舆情事件为例[J].电子政务,2021(9):23-35.(MA N, YU G, YAN X B. Taking the public opinion event of COVID-19 aid use as an example, research on the optimization method of government response strategy based on public opinion comment data mining-taking the public opinion event of COVID-19 aid use as an example[J].E-government,2021(9):23-35.)
|
| [18] |
齐佳音,方滨兴.重大突发事件中网络舆情引导及治理研究——以新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情为例[J].上海对外经贸大学学报,2020,27(3):5-13.(QI J Y, FANG B X. Network public opinion response and governance innovation in serious emergencies: take the COVID-19 epidemic as an example[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of International Business and Economics,2020,27(3):5-13.)
|
| [19] |
王李冬, 张慧熙. 基于HowNet的微博文本语义检索研究[J]. 情报科学, 2016,34(9):134-137.(WANG L D, ZHANG H X. Microblog text semantic retrieval based on HowNet[J].Information science,2016, 34(9): 134-137.)
|
| [20] |
崔彦琛,张鹏,兰月新,等. 面向时间序列的微博突发事件衍生舆情情感分析研究:以“6.22”杭州保姆纵火案衍生舆情事件为例[J]. 情报科学, 2019, 37(3): 119-126.(CUI Y C, ZHANG P, LAN Y X, et al. Time series-oriented study on the sentiment analysis of the derived public opinion for microblog emergencies[J]. Information science, 2019, 37(3): 119-126.)
|
| [21] |
台湾大学自然语言处理实验室.“NTUSD”[EB/OL].[2023-10-12].http://nlg.csie.ntu.edu.tw/.(Natural Language Processing Laboratory of Taiwan University.“NTUSD”[EB/OL].[2023-10-12].http://nlg.csie.ntu.edu.tw/.)
|
| [22] |
邱全磊,崔宗敏,喻静.基于表情和语气的情感词典用于弹幕情感分析[J].计算机技术与发展,2020,30(8):178-182.(QIU Q L, CUN Z M, YU J. Emotional dictionary based on emoticons and modal for barrage sentiment analysis[J].Computer technology and development,2020,30(8):178-182.)
|
| [23] |
李永帅,王黎明,柴玉梅,等.基于双向LSTM的动态情感词典构建方法研究[J].小型微型计算机系统,2019,40(3):503-509.(LI Y S, WANG L M, CHAI Y M, et al. Research on construction method of dynamic sentiment dictionary based on bidirectional LSTM[J].Journal of Chinese computer systems,2019,40(3):503-509.)
|
| [24] |
李静梅,孙丽华,张巧荣,等.一种文本处理中的朴素贝叶斯分类器[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报,2003(1):71-74.(LI J M, SUN L H, ZHANG Q R, et al. Application of native Bayes classifier to text classification[J].Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2003(1):71-74.)
|
| [25] |
ZHAO Q.Social emotion classification of Japanese text information based on SVM and KNN[J].Journal of Ambient intelligence and humanized computing,2021,8(6):1-12.
|
| [26] |
杨妥,李万龙,郑山红.融合情感分析与SVM_LSTM模型的股票指数预测[J].软件导刊,2020,19(8):14-18.(YANG T, LI W L, ZHENG S H. Stock index prediction based on SVM_LSTM model with emotion analysis[J].Software guide,2020,19(8):14-18.)
|
| [27] |
杨爽,陈芬.基于SVM多特征融合的微博情感多级分类研究[J].数据分析与知识发现,2017,1(2):73-79.(YANG S, CHENG F. Analyzing sentiments of micro-blog posts based on support vector machine[J].Data analysis and knowledge discovery,2017,1(2):73-79.)
|
| [28] |
KIM Y.Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[EB/OL].[2023-09-01].https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1408.5882.
|
| [29] |
程艳,尧磊波,张光河,等.基于注意力机制的多通道CNN和BiGRU的文本情感倾向性分析[J].计算机研究与发展,2020,57(12):2583-2595.(CHENG Y, YAO L B,ZHANG G H, et al. Text sentiment orientation analysis of multi-channels CNN and BiGRU based on attention mechanism[J].Journal of computer research and development,2020,57(12):2583-2595.)
|
| [30] |
冯传蕾.基于多模网络模型的个性化信息推荐算法及应用[J].微型电脑应用,2023,39(8):83-85.(FENG C L. Personalized information recommendation algorithm based on multimode network model and its application[J].Microcomputer applications,2023,39(8):83-85.)
|
| [31] |
BLEI D M, NG A Y, JORDAN M L,et al. Latent Dirichlet allocation[J]. Journal of machine learning research, 2003,3(4):993-1022.
|
| [32] |
蔡永明,长青.共词网络LDA模型的中文短文本主题分析[J].情报学报,2018,37(3):305-317.(CAI Y M, CHANG Q. Chinese short text topic analysis by Latent Dirichlet Allocation model with co-word network analysis[J].Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information,2018,37(3):305-317.)
|
| [33] |
安璐,杜廷尧,余传明,等.突发公共卫生事件的微博主题演化模式和时序趋势——以Twitter和Weibo的埃博拉微博为例[J].情报资料工作,2016(5):44-52.(AN L, DU T Y, YU C M, et al. Microblogging topic evolution pattern and timing trends of public health emergencies: taking Ebola microblogging on Twitter and Weibo for example[J].Information and documentation services,2016(5):44-52.)
|
| [34] |
ZHAO T T,LUO X F,QIN W, et al.Topic detection model in a single-domain corpus inspired by the human memory cognitive process[J].Concurrency and computation: practice and experience,2018,30(19):e4642.
|
| [35] |
赵常煜,吴亚平,王继民.“一带一路”倡议下的Twitter文本主题挖掘和情感分析[J].图书情报工作,2019,63(19):119-127.(ZHAO C Y, WU Y P, WANG J M. Twitter text topic mining and sentiment analysis under the belt and road lnitiative[J]. Library and information service,2019,63(19):119-127.)
|
| [36] |
胡万钟.从马斯洛的需求理论谈人的价值和自我价值[J].南京社会科学,2000(6):25-29.(HU W Z. On human value and self worth from Maslow's theory of needs[J].Nanjing journal of social sciences,2000(6):25-29.)
|
| [37] |
GAN C Q,FENG Q D,ZHANG Z F. Scalable multi-channel dilated CNN-BiLSTM model with attention mechanism for Chinese textual sentiment analysis[J].Future generation computer systems,2021,118(1):297-309.
|
| [38] |
赵成玉.突发公共事件中微博网民心理的态势感知及引导研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2020.(ZHAO C Y. Research on the situation awareness and guidance of Weibo netizens' psychology in public emergencies[D].Jinan: Shandong Normal University,2020.)
|
| [39] |
ASCH S E. Effects of group pressure upon the modification and distortion of judgments [J]. Journal of Marketing Research,1951,16(17):394-400.
|
| [40] |
王灵芝.网络舆情群体极化的心理学动因及二维效应[J].宜春学院学报,2015,37(5):34-39.(WANG L Z. Psychological inducements to group polarization for network public opinion and sentiment and analysis of its two-dimensional effects[J].Journal of Yichun University,2015,37(5):34-39.)
|
| [41] |
陈福集,张燕.基于E-Divisive的网络舆情演化分析[J].情报杂志,2016,35(4):75-79.(CHEN F J, ZHANG Y. Quantitative analysis method for long-term network public opinion events[J].Journal of intelligence,2016,35(4):75-79.)
|
郑杏冉:负责数据获取、文献调研分析及论文撰写;
黄卫东:负责论文选题、研究设计、核心框架设计,修改初稿。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |