 PDF(2435 KB)
PDF(2435 KB)


Research on Post-retraction Citations of COVID-19 Articles Based on Full-text Citation
Yanyu Ren, Siluo Yang
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2023, Vol. 8 ›› Issue (5) : 399-413.
 PDF(2435 KB)
PDF(2435 KB)
 PDF(2435 KB)
PDF(2435 KB)
Research on Post-retraction Citations of COVID-19 Articles Based on Full-text Citation
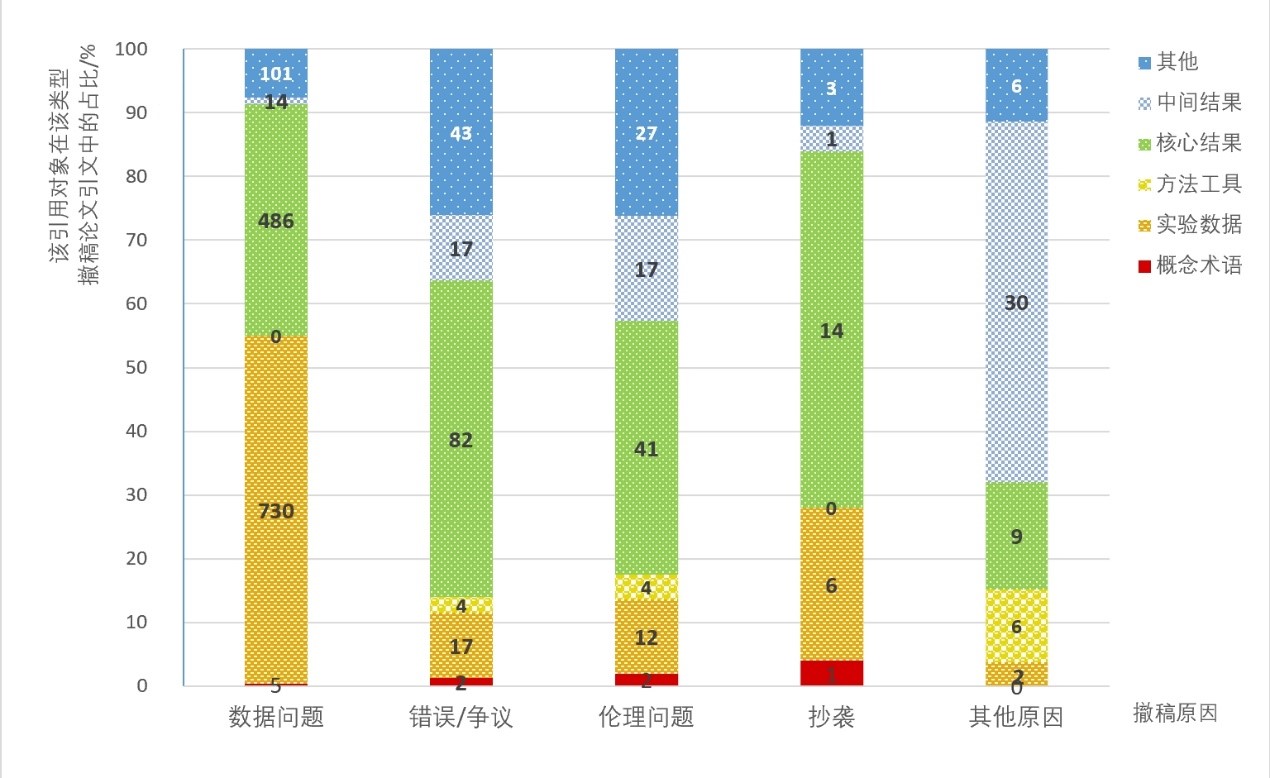
[Purpose/Significance] During the COVID-19 pandemic, many papers on this topic were withdrawn. But it was found through authoritative databases or websites that these papers have been cited even after the retraction. This study aims to analyze the dissemination and impact of retraction at the level of citation content, and to put forward suggestions on the optimization of citation and retraction mechanisms in major public events, in order to promote the healthy development of academic exchanges. [Method/Process] Firstly, the full text of COVID-19 retraction papers and citation references were obtained from WOS, Scopus, and PubMed databases, and the citation context in the citation references was manually extracted. Then, manual annotation and content analysis were carried out through the full-text citation analysis framework consisting of four dimensions: retraction mark situation, citation object, citation position, and citation emotion. [Result/Conclusion] The probability and speed of recognition of COVID-19 retracted papers are much higher than other papers in the biomedical field, and the retracted mechanism plays a certain role in academic purification. But its content continues to spread, with unreliability and misinformation spreading widely. This phenomenon should be paid enough attention by researchers, journals and databases, and the mechanism of citation and retraction in important public events should be optimized urgently.
COVID-19 / retracted papers / full-text citation analysis / academic purification / academic impact
| [1] |
GIANOLA S, JESUS T S, BARGERI S, et al. Characteristics of academic publications, preprints, and registered clinical trials on the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. PloS one, 2020, 15(10): e0240123
|
| [2] |
AVIV-REUVEN S, ROSENFELD A. Publication patterns’ changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal and short-term scientometric analysis[J]. Scientometrics, 2021, 126(8): 6761-6784.
|
| [3] |
PALAYEW A, NORGAARD O, SAFREED-HARMON K, et al. Pandemic publishing poses a new COVID-19 challenge[J]. Nature human behaviour, 2020, 4(7): 666-669.
|
| [4] |
李国琪.基于COVID-19论文撤稿特征探析期刊应对突发公共卫生事件的策略[J].天津科技,2022,49(5):90-95.(LI G Q. Analysis of reporting strategies of journals during public health emergencies based on characteristics of retracted COVID-19 papers[J].Tianjin science & technology,2022,49(5):90-95.)
|
| [5] |
姚长青,田瑞强,杨冬雨,等.撤销论文及其学术影响研究[J].中国科技期刊研究,2014,25(5):595-604.(YAO C Q, TIAN R Q, YANG D Y, et al. Research of retracted paper and its academic impact[J].Chinese journal of scientific and technical periodicals,2014,25(5):595-604.)
|
| [6] |
LONDON A J, KIMMELMAN J. Against pandemic research exceptionalism[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6490): 476-477.
|
| [7] |
BARROGA E, MATANGUIHAN G J. Fundamental shifts in research, ethics and peer review in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Journal of Korean medical science, 2020, 35(45): e395
|
| [8] |
SOLTANI P, PATINI R. Retracted COVID-19 articles: a side-effect of the hot race to publication[J]. Scientometrics, 2020, 125(1): 819-822.
|
| [9] |
DAGLIATI A, MALOVINI A, TIBOLLO V, et al. Health informatics and EHR to support clinical research in the COVID-19 pandemic: an overview[J]. Briefings in bioinformatics, 2021, 22(2): 812-822.
|
| [10] |
MHEIDLY N, FARES J. Leveraging media and health communication strategies to overcome the COVID-19 infodemic[J]. Journal of public health policy, 2020, 41(4): 410-420.
|
| [11] |
TEIXEIRA DA SILVA J A, TSIGARIS P, ERFANMANESH M. Publishing volumes in major databases related to Covid-19[J]. Scientometrics, 2021, 126(1): 831-842.
|
| [12] |
FRAMPTON G, WOODS L, SCOTT D A. Inconsistent and incomplete retraction of published research: a cross-sectional study on Covid-19 retractions and recommendations to mitigate risks for research, policy and practice[J]. PloS one, 2021, 16(10): e0258935.
|
| [13] |
SCHONHANT L, COSTA-ROLDAN I, OPPENHEIMER I, et al. Scientific publication speed and retractions of COVID-19 pandemic original articles[J].Pan American journal of public health , 2022, 46: e25.
|
| [14] |
YEO-TEH N S L, TANG B L. An alarming retraction rate for scientific publications on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)[J]. Accountability in research, 2021, 28(1): 47-53.
|
| [15] |
SHAMSI A, LUND B D, SEYYEDHOSSEINI S. Sharing of retracted COVID-19 articles: an altmetric study[J]. Journal of the Medical Library Association, 2022, 110(1): 97.
|
| [16] |
HAUNSCHILD R, BORNMANN L. Can tweets be used to detect problems early with scientific papers? A case study of three retracted COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 papers[J]. Scientometrics, 2021, 126(6): 5181-5199
|
| [17] |
PFEIFER M P, SNODGRASS G L. The continued use of retracted, invalid scientific literature[J]. Jama, 1990, 263(10): 1420-1423.
|
| [18] |
SCHNEIDER J, YE D, HILL A M, et al. Continued post-retraction citation of a fraudulent clinical trial report, 11 years after it was retracted for falsifying data[J]. Scientometrics, 2020, 125(3): 2877-2913.
|
| [19] |
KIM S Y, YI H J, CHO H M, et al. How many retracted articles indexed in KoreaMed were cited 1 year after retraction notification[J]. Science editing, 2019, 6(2): 122-127.
|
| [20] |
MADLOCK-BROWN C R, EICHMANN D. The (lack of) impact of retraction on citation networks[J]. Science and engineering ethics, 2015, 21(1): 127-137.
|
| [21] |
杨珠.造假论文被引分析——以国家自然科学基金委员会查处的造假论文为例[J].编辑学报,2022,34(3):291-294.(YANG Z. Citation analysis of Chinese falsified papers from the perspective of citation content analysis: taking the falsified paper investigated by the National Natural Science Foundation of China as an example[J]. Acta editologica,2022,34(3):291-294.)
|
| [22] |
BAR-ILAN J, HALEVI G. Post retraction citations in context: a case study[J]. Scientometrics, 2017, 113(1): 547-565.
|
| [23] |
袁子晗,张红伟.学术不端撤销论文施引文献引用态度分析——以哈佛大学心脏干细胞撤稿事件为例[J].中国科技期刊研究,2021,32(4):465-473.(YUAN Z H, ZHANG H W. Citation attitudes of articles to papers retracted due to academic misconducts: taking the retracted papers of cardiac stem cell from Harvard University as an example[J]. Chinese journal of scientific and technical periodicals,2021,32(4):465-473.)
|
| [24] |
VAN DER VET P E, NIJVEEN H. Propagation of errors in citation networks: a study involving the entire citation network of a widely cited paper published in, and later retracted from, the journal Nature[J]. Research integrity and peer review, 2016, 1(1): 1-10.
|
| [25] |
HAMILTON D G. Continued citation of retracted radiation oncology literature—Do we have a problem?[J]. International journal of radiation oncology biology physics, 2019, 103(5): 1036-1042.
|
| [26] |
石泽顺,肖明.基于本体和关联数据的全文引文分析方法研究[J].图书馆杂志,2021,40(4):100-108.(SHI Z S,XIAO M. Research on full-text citation analysis method based on ontology and linked data[J].Library journal,2021,40(4):100-108.)
|
| [27] |
崔红.我国科技人员引文动机聚类分析[J].情报杂志,1998(2):68-70.(CUI H. Clustering analysis of citation motivation of Chinese science and technology personnel[J].Journal of information,1998(2):68-70.)
|
| [28] |
TEUFEL S, SIDDHARTHAN A, TIDHAR D. Automatic classification of citation function[C]//Proceedings of the 2006 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Sydney: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2006: 103-110.
|
| [29] |
GARZONE M A. Automated classification of citations using linguistic semantic grammars[D].Canada: The University of Western Ontario,1997.
|
| [30] |
陆伟,孟睿,刘兴帮.面向引用关系的引文内容标注框架研究[J].中国图书馆学报,2014,40(6):93-104.(LU W, MENG R, LIU X B. A deep scientific literature mining-oriented framework for citation content annotation[J].Journal of library science in China,2014,40(6):93-104.)
|
| [31] |
张艺蔓,马秀峰,程结晶.融合引文内容和全文本引文分析的知识流动研究[J].情报杂志,2015,34(11):50-54,49.(ZHANG Y M, MA X F, CHENG J J. Research of knowledge flows based on citation content analysis[J]. Journal of intelligence,2015,34(11):50-54,49.)
|
| [32] |
刘运梅,马费成.面向全文本内容分析的文献三角引用现象研究[J].中国图书馆学报,2021,47(3):84-99.(LIU Y M, MA F C. Research on the phenomenon of literature triangular citation facing full text content analysis[J].Journal of library science in China,2021,47(3):84-99.)
|
| [33] |
杨思洛,聂颖.结合全文本分析的论文影响力评价模型研究[J].现代情报,2022,42(3):133-146.(YANG S L, NIE Y. Research on evaluation model of papers' influence combined with full-text analysis[J].Journal of modern information,2022,42(3):133-146.)
|
| [34] |
张春博,丁堃,王贤文,等.全文引文分析视角下的造假论文学术影响研究[J].科学学研究,2021,39(4):577-586.(ZHANG C B, DING K, WANG X W, et, al. Research on the impact of fraudulent paper to the academia from the view of citation analysis in full-text--case study of two highly cited retracted publications [J]. Studies in science of science,2021,39(4):577-586.)
|
| [35] |
LIU X, WANG C, CHEN D Z, et al. Exploring perception of retraction based on mentioned status in post-retraction citations[J]. Journal of informetrics, 2022, 16(3):101304.
|
| [36] |
曾建勋.我国学术期刊数据库的转型发展路径思考[J].编辑学报,2022,34(3):262-266.(ZENG J X. Thoughts on transformation and development path of China’s academic journal database[J].Acta editologica,2022,34(2):262-266)
|
| [37] |
吴任力,邓支青,吴淑倩.多维视域下开放获取期刊撤稿原因分析——基于Retraction Watch Database数据[J].中国科技期刊研究,2020,31(3):346-355.(WU R L, DENG Z Q, WU S Q. Analysis of the reasons for retraction of open access journals from multi-dimensional view: based on the data from Retraction Watch Database[J]. Chinese journal of scientific and technical periodicals, 2020,31(3):346-355.)
|
| [38] |
HORBACH S P J M. Pandemic publishing: medical journals strongly speed up their publication process for COVID-19[J]. Quantitative science studies, 2020, 1(3): 1056-1067.
|
| [39] |
BUDD J M, COBLE Z, ABRITIS A. An investigation of retracted articles in the biomedical literature[J]. Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 2016, 53(1): 1-9.
|
| [40] |
尹莉,邓红梅.自引的新评价——引用极性、引用位置和引用密度的视角[J].情报杂志,2019,38(9):180-184,179.(YIN L, DENG H M. New evaluation of self-citation: from the perspectives of reference polarity,reference position and reference density[J].Journal of intelligence,2019,38(9):180-184,179.)
|
| [41] |
SOMBATSOMPOP N, KOSITCHAIYONG A, MARKPIN T, et al. Scientific evaluations of citation quality of international research articles in the SCI database: Thailand case study[J]. Scientometrics, 2006, 66(3): 521-535.
|
| [42] |
吴宁,王传清,黄国彬.基于被引位置的数据论文价值分析——以数据期刊Scientific Data为例[J].图书情报研究,2022,15(2):41-49.(WU N, WANG C Q, HUANG G B. Value analysis of data papers based on cited location: taking scientific data as an example[J]. Library and information studies,2022,15(2):41-49.)
|
| [43] |
HU Z, CHEN C, LIU Z. Where are citations located in the body of scientific articles? a study of the distributions of citation locations[J]. Journal of informetrics, 2013, 7(4): 887-896.
|
| [44] |
HSIAO T K, SCHNEIDER J. Continued use of retracted papers: temporal trends in citations and (lack of) awareness of retractions shown in citation contexts in biomedicine[J]. Quantitative science studies, 2022, 2(4): 1144-1169.
|
| [45] |
刘晶晶.国外开放获取期刊的同行评议方式研究[J].编辑学报,2017,29(2):200-203.(LIU J J. Study of peer review modes of abroad open access journals[J].Acta editologica,2017,29(2):200-203.)
|
| [46] |
朱大明.关于科技学术期刊论文更正和撤销的讨论[J].编辑学报,2013,25(5):484-485.(ZHU D M. Erratum and revocation of papers in sci-tech academic journals[J].Acta editologica,2013,25(5):484-485.)
|
| [47] |
王丽丽.撤销论文被引用的原因探析及防范措施[J].出版发行研究,2018(8):74-76,64.(WANG L L. Analysis on the reasons for citations of retracted papers and preventive measures [J]. Publishing research,2018(8):74-76,64.)
|
| [48] |
刘燊,徐飞.NSC杂志撤稿论文引用异常增加现象辨析与治理建议[J].中国科技期刊研究,2022,33(5):545-553.(LIU S,XU F. Analysis of the abnormal increase in cited frequency of retracted papers in NSC and suggestions for governance[J]. Chinese journal of scientific and technical periodicals,2022,33(5):545-553.)
|
| [49] |
HILL A, GARRATT A, LEVI J, et al. Retracted: meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection[J].Open forum infectious diseases,2021, 8(11): ofab358.
|
任檐雨:进行研究选题与设计,收集与分析数据,撰写论文;
杨思洛:提出研究方向,指导与修订论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |