 PDF(1292 KB)
PDF(1292 KB)


The Psychological Perception and Usage Behavior of Elderly Users on Smart Health Care Products——A Study of Grounded Theory Based on Text Information
Li Huaqiang, Hu Dongmei
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2023, Vol. 8 ›› Issue (2) : 104-114.
 PDF(1292 KB)
PDF(1292 KB)
 PDF(1292 KB)
PDF(1292 KB)
The Psychological Perception and Usage Behavior of Elderly Users on Smart Health Care Products——A Study of Grounded Theory Based on Text Information
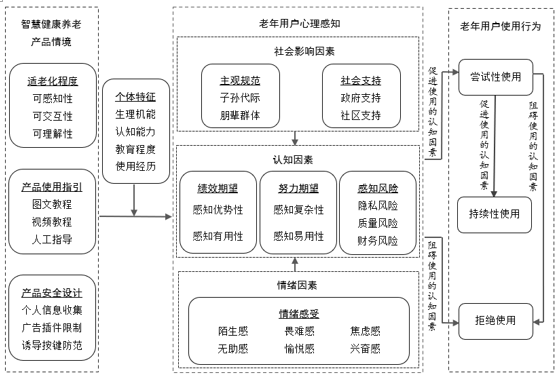
[Purpose/Significance] Under the background of the rapid development of the new generation of information technology, the policy supports the smart health care industry, and all kinds of smart health care products are constantly popularized and applied. Exploring the practical issue of elderly users using smart health care products is of great significance for China to carry out smart actions to help the elderly and build a digital inclusive old-age society. [Method/Process] Based on the text information data such as news reports, product reviews and in-depth interviews, this paper adopted the grounded theory method, and formed 3 relational categories, 31 preliminary categories and 69 initial concepts through three-stage coding, and constructed a model of influencing factors of elderly users’ use of smart health care products. [Result/Conclusion] The research showed that the aging degree, product use guidelines and product safety design affect the psychological perception of elderly users, and individual characteristics will adjust their perception. The psychological perception of the elderly includes subjective norms, social support, performance expectations, effort expectations, perceived risks and emotional feelings, which influence the formation of 3 different use behaviors: trial use, persistent use and refusal to use. Finally, some feasible suggestions were put forward from 3 aspects: improving the aging degree of smart health care products, guiding the psychological perception of the elderly users, and enhancing the use skills of the elderly users.
elderly users / smart health care products / psychological perception / usage behavior / grounded theory
| [1] |
ZANDIEH R, ACHEAMPONG R A. Mobility and healthy ageing in the city: exploring opportunities and challenges of autonomous vehicles for older adults’ outdoor mobility[J]. Cities, 2021, 112: 103135.
|
| [2] |
SANTHANARAJ K K, RAMYA M M, DINAKARAN D. A survey of assistive robots and systems for elderly care[J]. Journal of enabling technologies, 2021, 15(1): 66-72.
|
| [3] |
PURAO S, HAO H, MENG C. The use of smart home speakers by the elderly: exploratory analyses and potential for big data[J]. Big data research, 2021, 25: 100224.
|
| [4] |
DAVIS F D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease, and user acceptance of information technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 1989, 13(3): 319-340.
|
| [5] |
VENKATESH V, DAVIS F D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies[J]. Management science, 2000, 46(2): 186-204.
|
| [6] |
VENKATESH V, MORRIS M G, DAVIS G B, et al. User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view[J]. MIS quarterly, 2003, 27(3): 425-478.
|
| [7] |
VENKATESH V, BALA H. Technology acceptance model 3 and a research agenda on interventions[J]. Decision sciences, 2008, 39(2): 273-315.
|
| [8] |
VENKATESH V, THONG J, XU X. Consumer acceptance and use of Information technology: extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology[J]. MIS quarterly, 2012, 36(1): 157-178.
|
| [9] |
韩啸. 整合技术接受模型的荟萃分析:基于国内10年研究文献[J]. 情报杂志, 2017, 36(8): 150-155,174.
|
| [10] |
张培. 技术接受模型的理论演化与研究发展[J]. 情报科学, 2017, 35(9): 165-171.
|
| [11] |
李彪. 数字反哺与群体压力:老年群体微信朋友圈使用行为影响因素研究[J]. 国际新闻界, 2020, 42(3): 32-48.
|
| [12] |
MIHA C, MAJA M B, PETER T. Analyzing older users’ home telehealth services acceptance behavior—applying an extended UTAUT model[J]. International journal of medical informatics, 2016, 90: 22-31.
|
| [13] |
GHORAYEB A C R, GOOBERMAN-HILL R. Older adults' perspectives of smart home technology: are we developing the technology that older people want?[J]. International journal of human-computer studies, 2021, 147: 102571.
|
| [14] |
刘晓静, 罗椅民. 深度老龄化背景下我国适老辅具技术:应用、适配评估与发展研究[J]. 中国软科学, 2021(2): 57-64.
|
| [15] |
贺建平, 黄肖肖. 城市老年人的智能手机使用与实现幸福感:基于代际支持理论和技术接受模型[J]. 国际新闻界, 2020, 42(3): 49-73.
|
| [16] |
CHEN Z, QI H Y, WANG L M. Study on the types of elderly intelligent health management technology and the influencing factors of its adoption[J]. Healthcare, 2021, 9(11): 1494.
|
| [17] |
FILIPPO C, RAFFAELE E, RAFFAELE L, et al. Robotic services acceptance in smart environments with older adults: user satisfaction and acceptability study[J]. Journal of medical internet research, 2018, 20(9): e264.
|
| [18] |
ANDRé B P, INGE H G, KARSTEN R O, et al. Smartphone usage among older adults[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2021, 121: 106783.
|
| [19] |
LI J, MA Q, CHAN A H, et al. Health monitoring through wearable technologies for older adults: smart wearables acceptance model[J]. Applied ergonomics, 2019, 75: 162-169.
|
| [20] |
马琪, 陈浩鑫. 智慧养老技术接受与政策助推路径初探——基于2005—2020年国内外文献的系统性整合分析[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2021(4): 161-170.
|
| [21] |
MEHRABIAN A, RUSSELL J A. An approach to environmental psychology[M]. Cambrige: MIT Press, 1974: 30-35.
|
| [22] |
张德鹏, 陈春峰, 张凤华. 社交媒体情境下个性化广告对用户态度的影响研究[J]. 管理学报, 2021, 18(3): 441-447.
|
| [23] |
王文韬, 张震, 张坤, 等. 融合SOR理论的智能健康手环用户不持续使用行为研究[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2020, 40(5): 92-102.
|
| [24] |
SONG S J, YAO X l, WEN N N. What motivates Chinese consumers to avoid information about the COVID-19 pandemic? the perspective of the stimulus-organism-response model[J]. Information processing & management, 2021, 58(1): 102407.
|
| [25] |
罗琳, 杨洋. 社会化标注系统中用户标签使用行为影响因素研究[J]. 图书情报知识, 2018(3): 85-94.
|
| [26] |
GLASER B G, STRAUSS A L, STRUTZEL E. The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research[J]. Nursing research, 1968, 17(4): 377-380.
|
| [27] |
工业和信息化部 民政部 国家卫生健康委员会. 关于公布《智慧健康养老产品及服务推广目录(2018年版)》的通告[EB/OL]. [2022-06-01]. https://www.miit.gov.cn/zwgk/zcwj/wjfb/tg/art/2020/art_f3a91187917d47258f88436fb23a25bc.html.
|
| [28] |
工业和信息化部 民政部 国家卫生健康委员会. 关于公布《智慧健康养老产品及服务推广目录(2020年版)》的通告[EB/OL]. [2022-06-01]. https://www.miit.gov.cn/zwgk/zcwj/wjfb/dzxx/art/2020/art_4092629bb22840ecb56ffe51bf0d9120.html.
|
| [29] |
李贺楼. 扎根理论方法与国内公共管理研究[J]. 中国行政管理, 2015(11): 76-81.
|
| [30] |
李辉, 黄雅卓, 徐美宵, 等. “避害型”府际合作何以可能?——基于京津冀大气污染联防联控的扎根理论研究[J]. 公共管理学报, 2020, 17(4): 53-61,109,168.
|
| [31] |
CORBIN J M, STRAUSS A. Grounded theory research: procedures, canons, and evaluative criteria[J]. Qualitative sociology, 1990, 13(1): 3-21.
|
| [32] |
钱宇星, 李浩, 倪珍妮, 等. 论坛式网络信息服务适老化困境与应对——以“银龄网”关停为例[J]. 图书情报知识, 2021(2): 68-78,109.
|
| [33] |
刘杰, 郭超. 移动互联网应用程序(APP)使用对老年人身心健康的影响——以微信、微信朋友圈和手机支付的使用为例[J]. 人口与发展, 2021, 27(6): 117-128.
|
| [34] |
窦金花, 覃京燕. 智慧健康养老产品适老化设计与老年用户研究方法[J]. 包装工程, 2021, 42(6): 62-68.
|
| [35] |
李连友, 李磊, 邓依伊. 中国家庭养老公共政策的重构——基于家庭养老功能变迁与发展的视角[J]. 中国行政管理, 2019(10): 112-119.
|
李华强:设计研究架构,进行模型阐释,撰写论文;
胡冬梅:进行文本数据分析,撰写与修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |