 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)


Research on Note-Taking Tools for Scientific Work
Wang Shuyi, Cui Leiyue, Shi Ying, Wang Zheng
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2022, Vol. 7 ›› Issue (6) : 652-661.
 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)
 PDF(1473 KB)
PDF(1473 KB)
Research on Note-Taking Tools for Scientific Work
[Purpose/Significance] This paper aims to analyze the characteristics and advantages of digital note tools, so as to remove the obstacles encountered in the process of scientific research, dredge the scientific research process, and improve the scientific research efficiency. [Method/Process] Through literature analysis, network research and other methods, we sought relevant note-taking tools for the common pain points in scientific research activities, and explored its functional advantages as the starting point. [Result/Conclusion] It is finally concluded that digital note-taking tools have considerable advantages in auxiliary supplementing human brain functions, solving process inefficiency and building knowledge networks, and can achieve the goal of enabling scientific research.
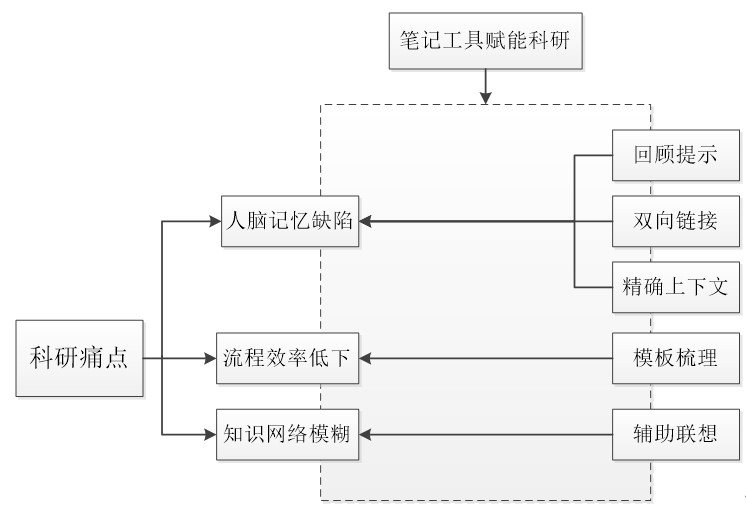
knowledge management / note application / research efficiency / research empowerment
| [1] |
SWAR B, HAMEED T, REYCHAV I. Information overload, psychological ill-being, and behavioral intention to continue online healthcare information search[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2017, 70(5): 416-425.
|
| [2] |
陈琼,宋士杰,赵宇翔.突发公共卫生事件中信息过载对用户信息规避行为的影响:基于COVID-19信息疫情的实证研究[J].情报资料工作,2020,41(3):76-88.
|
| [3] |
SWEENY K, MELNYK D, MILLER W, et al. Information avoidance: who, what, when, and why[J]. Review of general psychology, 2010, 14(4): 340-353.
|
| [4] |
KRIGOLSON O E, HEINEKEY H, KENT C M, et al. Cognitive load impacts error evaluation within medial-frontal cortex[J]. Brain research, 2012, 1430(1): 62-67.
|
| [5] |
BADDELEY A. Working memory: looking back and looking forward[J]. Nature reviews neuroscience, 2003, 4(10): 829-839.
|
| [6] |
MARTI E, JEANNE M. The concept of information overload: a review of literature from organization science, accounting, marketing, MIS, and related disciplines[J]. The information society, 2004, 20(5) : 325-344.
|
| [7] |
潘曙光.信息偶遇研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2010.
|
| [8] |
万力勇,斯坦.基于信息偶遇的在线偶发学习:内在机理与影响因素[J].中国电化教育,2019(12):78-86.
|
| [9] |
刘文剑,金天国.产品自顶向下设计的研究现状及发展方向[J].计算机集成制造系统,2002(1):1-7..
|
| [10] |
马培培.知识管理视域下数字化笔记工具的比较研究[D].上海:上海师范大学,2012.
|
| [11] |
连明.信息碎片化时代的大学生信息素养[J].农业网络信息,2018(6):115-119.
|
| [12] |
常李艳,陈思璐,刘婧,等.信息碎片化环境下大学生移动学习行为影响因素研究[J].中国教育信息化,2022,28(5):50-58.
|
| [13] |
蔺丰奇,刘益.网络化信息环境中信息过载问题研究综述[J].情报资料工作,2007(3):36-41,48.
|
| [14] |
魏娟,李敏.信息过载影响消费者决策研究的知识图谱分析[J].管理现代化,2022,42(1):156-161.
|
| [15] |
李卓昆.探究学习中降低认知负荷的策略研究[D].保定:河北大学,2008.
|
| [16] |
帖伊,张文杰.从认知超负荷模式看口译中的信息差及其调控策略[J].赤峰学院学报(科学教育版),2011,3(8):108-109.
|
| [17] |
WOLF G. The curse of Xanadu[J]. Wired, 1995, 3(6): 137.
|
| [18] |
陈力行.论个人知识管理[J].情报科学,2005(7):1072-1075.
|
| [19] |
王延秋.终身学习时代的图书馆个人知识管理[J].情报杂志,2003(9):75-76,79.
|
| [20] |
陈思义.试论个人知识管理工具[J].数字与缩微影像,2022(1):40-43.
|
| [21] |
王佳敏.思维导图在碎片化学习的个人知识管理中的应用[J].信息与电脑(理论版),2020,32(21):207-209.
|
| [22] |
苏媛欣.数字化笔记在个人知识管理中的应用[J].知识管理论坛,2015(1):35-41.
|
| [23] |
ARTZ B, JOHNSON M, ROBSON D, et al. Taking notes in the digital age: evidence from classroom random control trials[J]. The journal of economic education, 2020, 51(2): 103-115.
|
| [24] |
OSMAN M A, NOAH S A M, SAAD S. Ontology-based knowledge management tools for knowledge sharing in organization—a review[J]. IEEE access, 2022, 10(1): 43267-43283.
|
| [25] |
COURTNEY M, COSTLEY J, BALDWIN M, et al. Individual versus collaborative note-taking: results of a quasi-experimental study on student note completeness, test performance, and academic writing[J]. The internet and higher education, 2022, 55(7): 100873.
|
| [26] |
王树义,张晋,李峻.图数据库驱动的知识管理应用特性对比研究——以Roam Research为例[J].知识管理论坛,2021,6(5):292-301.
|
| [27] |
Flomo:version1.7.0[EB/OL].[2022-09-12]. https://flomoapp.com.
|
| [28] |
Logseq:version0.6.7[EB/OL].[2022-09-12]. https://logseq.com.
|
| [29] |
Hook:version3.7.1[EB/OL].[2022-09-12]. https://hookproductivity.com.
|
| [30] |
DevonThink:version3.3.4[EB/OL] .[2022-09-12].https://www.devontechnologies.com/apps/devonthink.
|
| [31] |
How JISC is helping researchers [EB/OL] .[2022-09-10].http://www.jisc.ac.uk/whatw -edo/campaigns/res3/jischelp.aspx.
|
王树义:提出框架,拟定框架,修改文稿
崔雷悦:采集资料,起草文稿
时莹:采集资料,修改文稿
王铮:修改文稿
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |