 PDF(2131 KB)
PDF(2131 KB)


An Evolutionary Game Analysis of Doctor-Patient Online Interaction based on Reputation Feedback Mechanism
Li Meiyu, Xu Xin
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2022, Vol. 7 ›› Issue (5) : 562-573.
 PDF(2131 KB)
PDF(2131 KB)
 PDF(2131 KB)
PDF(2131 KB)
An Evolutionary Game Analysis of Doctor-Patient Online Interaction based on Reputation Feedback Mechanism
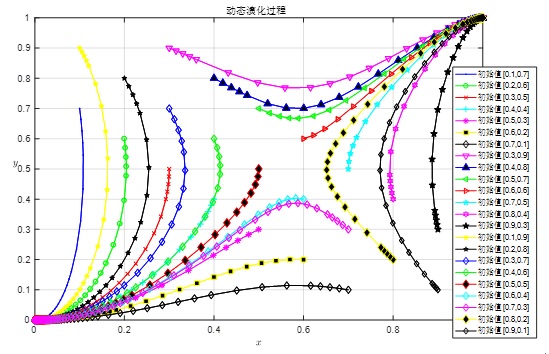
[Purpose/Significance] Online reputation is an important regulating mechanism to maintain the order of online medical care. Through exploring the internal mechanism of online reputation feedback mechanism on doctor-patient interaction, this paper provided strategies for improving the supervision and management of online medical community. [Method/Process] The finite rational evolutionary game model between doctors and patients was constructed. The dynamic equation was calculated, the equilibrium and stability strategy was solved, and the Matlab software was used for simulation analysis to find out the key influencing factors and influencing paths of promoting doctor-patient online positive interaction. [Result/Conclusion] The results show that the degree to which negative evaluation behavior can alleviate patients' dissatisfaction, the cost of doctors' positive response, and the frustration of doctors' enthusiasm being depressed have a negative effect on doctor-patient interaction. The information gap reduced by correct information feedback of patients and doctors' mental incentive to be recognized have a positive effect on doctor-patient interaction.
online medical treatment / reputation feedback / incentive mechanism / doctor-patient interaction / evolutionary game theory
| [1] |
中国互联网网络信息中心. 第50次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》[EB/OL].[2022-10-24]. http://www.cnnic.cn/n4/2022/0914/c88-10226.html..
|
| [2] |
ZHAI Y, GE X, LIU X, et al. An internet-based multidisciplinary online medical consultation system to help cope with pediatric medical needs during the COVID-19 outbreak: a cross-sectional study[J]. Translational pediatrics, 2021, 10(3):560-568.
|
| [3] |
周敏, 郅慧. 信息精细加工可能性模型对公众在线择医意愿影响研究[J]. 教育传媒研究,2021(1):38-42.
|
| [4] |
WANG P, WANG J, LI Q. Cognitive mechanisms underlying interaction and contribution in online health communities: the perspectives of doctors and patients[J]. Aslib journal of information management, 2021, 73(3):367-385.
|
| [5] |
MCGEADY D, KUJALA J, ILVONEN K. The impact of patient–physician Web messaging on healthcare service provision [J]. International journal of medical informatics, 2008, 77(1): 17-23.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG J, WANG, K. et al. Should doctors use or avoid medical terms? the influence of medical terms on service quality of e-health[J/OL]. Electronic commerce research,2021.[2022-04-19]. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10660-021-09516-6#citeas.
|
| [7] |
CHEN S, GUO X, WU T, et al. Exploring the online doctor-patient interaction on patient satisfaction based on text mining and empirical analysis[J]. Information processing & management, 2020, 57(5): 102-253.
|
| [8] |
NAVEH S, BRONSTEIN J. Sense making in complex health situations: virtual health communities as sources of information and emotional support[J]. Aslib journal of information management, 2019, 71(6):789-805.
|
| [9] |
张星, 陈星, 夏火松, 等.在线健康社区中用户忠诚度的影响因素研究:从信息系统成功与社会支持的角度[J].情报科学,2016,36(3):133-138.
|
| [10] |
ARORA N K, WEAVER K E, CLAYMAN M L, et al. Physicians’ decision-making style and psychosocial outcomes among cancer survivors[J]. Patient education and counseling, 2009, 77(3): 404-412.
|
| [11] |
王瑜超, 孙永强. 服务和互惠规范对于在线医疗社区用户自我表露意愿的影响研究[J]. 情报科学,2018,36(5):149-157.
|
| [12] |
HALUZA D, JUNGWIRTH D. ICT and the future of healthcare: aspects of pervasive health monitoring[J]. Informatics for health and social care, 2018,43(1): 1-11.
|
| [13] |
OKORO O E, MBAH I O. Use of social media in doctor–patient relationship by patients in federal medical center, keffi, north-central nigeria[J] Journal of consumer health on the internet, 2021,25(3): 230-241.
|
| [14] |
郝亚楠, 郭文秀, 贺培凤, 等.患者信息搜寻行为的调查分析[J].晋图学刊,2011(6):63-67.
|
| [15] |
吴红. 基于服务提供与定价视角的在线医患多阶段交互机制研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2019.
|
| [16] |
LIU J, HOU S, EVANS R, et al. What do patients complain about online: a systematic review and taxonomy framework based on patient centeredness[J]. Journal of medical internet research, 2019, 21(8):e14634.
|
| [17] |
李士梅, 高维龙. 契约视角下政府委托第三方提供养老服务的激励约束机制分析[J].内蒙古社会科学(汉文版),2018,39(2):117-124,2.
|
| [18] |
YANG R, WANG D. Hierarchical aggregation for reputation feedback of services networks[J]. Mathematical problems in engineering, 2020(1):1-12.
|
| [19] |
KRAWCKE N. Effectively managing your company's online reputation[J]. Air conditioning, heating & refrigeration news, 2018, 263(14):4-4.
|
| [20] |
GAO G G,MC CULLOUGH J S,AGARWAL R,et al. A changing landscape of physician quality reporting: analysis of patients’ online ratings of their physicians over a 5-year period [J]. Journal of medical internet research,2012, 14 (1) : 38-46.
|
| [21] |
陆泉, 李易时, 陈静, 等. 在线医疗社区患者择医行为影响因素研究[J]. 图书情报工作,2019,63(8):87-95.
|
| [22] |
姜劲, 白闪闪, 王云婷, 等. 线上和线下医疗服务质量对患者线下就医决策的影响[J].管理科学,2020, 33(1):46-53.
|
| [23] |
张梦林, 李玉玲, 申宁宁, 等. 齐齐哈尔市某三甲医院医生职业认同与工作压力、应对方式的关系研究[J]. 医学与社会,2019,32(6):107-110.
|
| [24] |
董霏, 罗园园.医生心理健康状况与应对方式的初步研究[J].职业与健康,2006(3):161-165.
|
| [25] |
YAN Z J,WANG T M,CHEN Y,et al. Knowledge sharing in online health communities:a social exchange theory perspective[J]. Information & management,2016,53(5):643-653.
|
| [26] |
ZHANG X,LIU S. Understanding relationship commitment and continuous knowledge sharing in online health communities:a social exchange perspective[J/OL]. Journal of knowledge management,2021,17(12):1123-1147 [2022-04-28].https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-12-2020-0883.
|
李美玉:撰写、修改和完善论文
许鑫:论文框架的指导与确定
感谢华东师范大学侯经川教授和南京大学赵月华博士提出修改意见。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |