 PDF(1033 KB)
PDF(1033 KB)


Meta-ethnography: A Qualitative Research Method of Effective Comprehensive Integration
Yang Yuqi
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2020, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (5) : 329-336.
 PDF(1033 KB)
PDF(1033 KB)
 PDF(1033 KB)
PDF(1033 KB)
Meta-ethnography: A Qualitative Research Method of Effective Comprehensive Integration
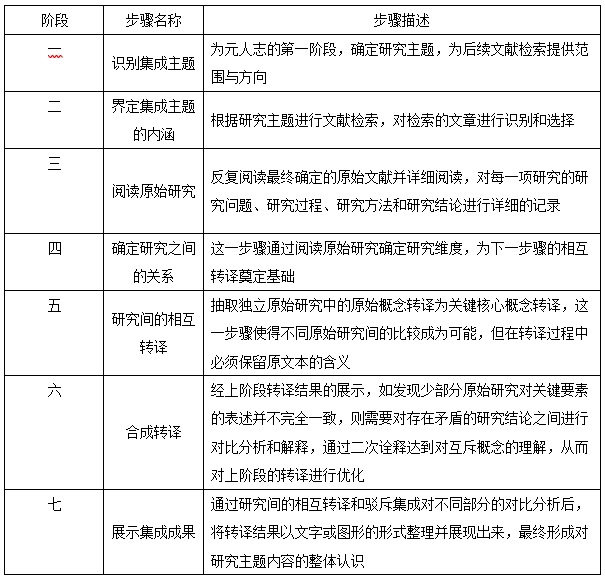
[Purpose/significance] Qualitative research method is an important part of academic research. This research mathematically summarizes the relevant research results of meta ethnography at home and abroad, and forms a relatively complete theoretical content, which provides a reference for scholars in the field of information behavior and other fields to choose research methods in the future. [Method/process] Based on the multi-disciplinary perspective, this paper used Web of Science to retrieve the related literature of meta-ethnography research methods, and used bibliometrics and content analysis to summarize the research status and application of meta-ethnography methods, in which the application part focused on introducing the research of meta-ethnography in the field of information behavior. [Results/conclusion] The meta-ethnographic method is one of the important methods for qualitative research, and there are few domestic studies on the use of meta-ethnographic method. This study summarizes the development history of meta-ethnography, the differences from other methods, applicable types and characteristics, implementation steps, and the application results of this method in existing disciplines, which will help scholars to fully understand the research methods of meta-ethnography.
| [1] |
NOBLIT G W, HARE R D. Meta-ethnography:issues in the synthesis and replication of qualitative research[C/OL]// Proceedings of 67th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association[2020-08-24]. http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED231853.pdf.
|
| [2] |
NOBLIT G W, HARE R D. Meta-ethnography: Synthesizing qualitative studies[M]. Newbury Park: Sage, 1998.
|
| [3] |
周林. 元分析方法简介[J]. 心理发展与教育,1992(2):27-31.
|
| [4] |
CAMPBELL R, POUND P, POPE C, et al. Evaluating meta-ethnography: a synthesis of qualitative research on lay experiences of diabetes and diabetes care[J]. Social science & medicine, 2003, 56(4):671-684.
|
| [5] |
TOYE F, SEERS K, ALLCOCK N, et al. Meta-ethnography 25 years on: challenges and insights for synthesising a large number of qualitative studies[J]. BMC medical research methodology, 2014, 14(1):80-94.
|
| [6] |
CAMPBELL R, POUND P, MORGAN M. Evaluating meta-ethnography: systematic analysis and synthesis of qualitative research [J]. Health technology assessment, 2011, 15(43):1-164.
|
| [7] |
FRANCE E F, WELLS M, LANG H, et al. Why, when and how to update a meta-ethnography qualitative synthesis[J]. Systematic reviews, 2016, 5(1):44-56.
|
| [8] |
LEVACK W M M. The role of qualitative metasynthesis in evidence-based physical therapy[J]. Physical therapy reviews, 2012, 17(6):390-397.
|
| [9] |
RING N, JEPSON R, PINNOCK H, et al. Developing novel evidence-based interventions to promote asthma action plan use: a cross-study synthesis of evidence from randomised controlled trials and qualitative studies[J]. Trials, 2012, 13(1):216-216.
|
| [10] |
WALSH M , GALVIN R , HORGAN N F . Fall-related experiences of stroke survivors: a meta-ethnography[J]. Disability and rehabilitation, 2017, 39(7):10.
|
| [11] |
ALLISON T , KATE F , ELIZABETH M I , et al. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ[J]. BMC medical research methodology, 2012, 12(1):181-181.
|
| [12] |
MUNRO S A , LEWIN S A , SMITH H J , et al. Patient adherence to tuberculosis treatment: a systematic review of qualitative research[J]. PLOS medicine, 2007, 4(7):1230-1245.
|
| [13] |
SMITH L K , PPOE C , BOTHA J L . Patients' help-seeking experiences and delay in cancer presentation: a qualitative synthesis[J]. Lancet, 2015, 366(9488):825-831.
|
| [14] |
ATKINS S , LEWIN S , SMITH H , et al. Conducting a meta-ethnography of qualitative literature: lessons learnt[J]. BMC medical research methodology, 2008, 8(1):1-10.
|
| [15] |
MALPASS A , SHAW A , SHARP D , et al. “Medication career” or “moral career”? the two sides of managing antidepressants: a meta-ethnography of patients’ experience of antidepressants[J]. Social science & medicine, 2009, 68(1):154-168.
|
| [16] |
MAIR F S , MAY C , CATHERINE O D, et al. Factors that promote or inhibit the implementation of e-health systems: an explanatory systematic review[J]. Bulletin of the world health organization, 2012, 90(5):357-364.
|
| [17] |
SIAU K , LONG Y . Synthesizing e‐government stage models – a meta‐synthesis based on meta‐ethnography approach[J]. Industrial management & data systems, 2005, 105(4):443-458.
|
| [18] |
TONDEUR J , BRAAK J V , SANG G , et al. Preparing pre-service teachers to integrate technology in education: a synthesis of qualitative evidence[J]. Computers & education, 2012, 59(1):1-144.
|
| [19] |
SANDERS C, BISAILLON L. When health care is displaced by state interests: building dialogue through share findings[J].Qualitative health research, 2019,1(29):32-41.
|
| [20] |
BHATTACHARYA A, CAMACHO D,KIMBERLY LL,et al. Women's experiences and perceptions of depression in India: a metaethnography[J]. Qualitative health research, 2019,29(1):80-95.
|
| [21] |
BRITTEN N, GARSIDE R, POPE C, et al. Asking more of qualitative synthesis: a response to sally thorne[J]. Qualitative health research, 2017, 27(9):1370-1390.
|
| [22] |
BONDAS T , HALL E O C . Challenges in approaching metasynthesis research[J]. Qualitative health research, 2007, 17(1):113-121.
|
| [23] |
URQUHART C . Meta-synthesis of research on information seeking behaviour[J]. Information research, 2011, 16(1):95-116.
|
| [24] |
LINDENMEYER A , GREENFIELD S M , GREENFIELD C , et al. How do people With COPD value different activities? an adapted meta-ethnography of qualitative research[J]. Qualitative health research, 2016:1-14.
|
| [25] |
SKAGEBY J. The irony of serendipity: disruptions in social information behaviour[J]. Library Hi Tech, 2012, 30(2):321-334.
|
| [26] |
YAHYAPOUR S , SHAMIZANJANI M , MOSAKHANI M . A conceptual breakdown structure for knowledge management benefits using meta-synthesis method[J]. Journal of knowledge management, 2015, 19(6):1295-1309.
|
| [27] |
周佩, 黄春燕. 信息偶遇研究元人种志分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2014,58(14):115-120.
|
| [28] |
SHALLCROSS R , DICKSON J M , NUNNS D , et al. Women’s subjective experiences of living with Vulvodynia: a systematic review and Meta-Ethnography[J]. Archives of sexual behavior, 2017,47(40):123-142.
|
| [29] |
WIKBERG A , BONDAS T . A patient perspective in research on intercultural caring in maternity care: a meta-ethnography[J]. International journal of qualitative studies on health and well-being, 2010, 5(1):1-16.
|
| [30] |
TOMBOR I , SHAHAB L , HERBEC A , et al. Smoker identity and its potential role in young adults’ smoking behavior: a Meta-Ethnography[J]. Health psychology, 2015, 34(10): 992-1003.
|
| [31] |
WILLIAMS S, RENJU J, GHILARDI L , et al. Scaling a waterfall: a meta-ethnography of adolescent progression through the stages of HIV care in sub-Saharan Africa[J]. Journal of the international AIDS society, 2017, 20(1):1-17.
|
| [32] |
WAHID A S , SAYMA M , JAMSHAID S , et al. Barriers and facilitators influencing death at home: a meta-ethnography[J]. Palliative medicine, 2017,32(7):1-15.
|
| [33] |
LAWRENCE C. A holistic narrative of culture's mediation of information systems innovation: A qualitative Meta-Synthesis[J]. Journal of global information technology management, 2014, 16(3):31-52.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |