 PDF(1155 KB)
PDF(1155 KB)


Research on the Establishment of Cross-Region Emergency Decision Support System under the Context of Social Media
Wenting Lu
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2019, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4) : 246-255.
 PDF(1155 KB)
PDF(1155 KB)
 PDF(1155 KB)
PDF(1155 KB)
Research on the Establishment of Cross-Region Emergency Decision Support System under the Context of Social Media
[Purpose/significance] The rapid development of social media, social network, micro-blog and other social mediahave brought new opportunities and challenges to emergency management. Related works will not only fulfill and extend present theories in fields of emergency management, but also provide scientific basis and guidance for the cross-region emergency decision. [Method/process] On the basis of the careful consideration on the characteristics of social media data and the existing problems faced by cross-region emergency decision, a novel cross-region emergency decision supportframework based on multiple information sources fusion is proposed and constructed. Then five key issues for the perfection of the cross-region emergency decision support system are probed, and countermeasures are briefly presented. [Results/conclusion] Introducing dynamic web social media information into cross-region emergency decision and integrating it with other emergency information will help to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of emergency decision,which will play an active role in emergency decision analysis and emergency management.
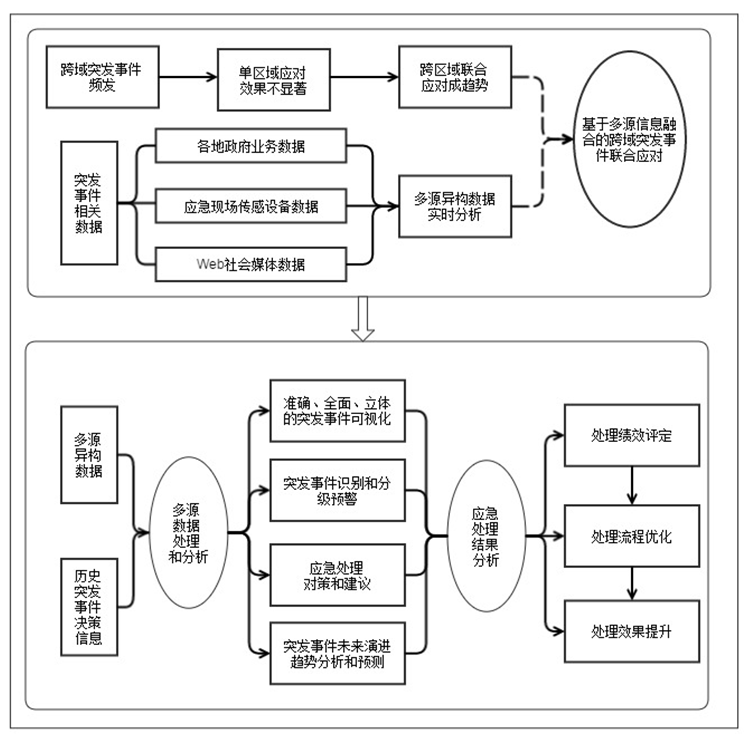
social media / emergent events / emergency decision support / multiple information sources fusion
| [1] |
陈进峰. 我国防灾减灾科技应用与建设的现状、问题及建议[J]. 城乡建设,2008(8):54-55.
|
| [2] |
曾大军,曹志冬.突发事件态势感知与决策支持的大数据解决方案[J].中国应急管理, 2013(11):15-23.
|
| [3] |
王宏伟. 构建京津冀跨域突发事件应急联动的有效机制[J]. 中国应急救援,2017(5),18-23.
|
| [4] |
刘丹,王红卫,祁超,等. 基于多主体的应急决策组织建模[J]. 公共管理学报,2013(4):78-87.
|
| [5] |
BHAROSA N, LEE J K, JANSSEN M. Challenges and obstacles in sharing and coordinating information during multi-agency disaster response: propositions from field exercises[J]. Information systems frontiers, 2010, 12(1):49-65.
|
| [6] |
谭小群,陈国华. 美国应急管理合作对我国跨区域应急管理的启示[J].工业安全与环保,2011,37(10):51-53.
|
| [7] |
王庆明. 建立环渤海地区应急管理协调联动机制的对策[J].中共济南市委党校学报,2013(1):81-84.
|
| [8] |
严蓉. 组织间目标差异对组织间应急合作关系的影响研究——基于沟通的中介作用[D].武汉:武汉纺织大学,2014.
|
| [9] |
蒋勋,苏新宁,周鑫. 适应情景演化的应急响应知识库协同框架体系构建[J]. 图书情报工作,2017,61 (15) : 60-71.
|
| [10] |
邹逸江. 国外应急管理体系的发展现状及经验启示[J]. 灾害学, 2008, 23(1):96-101.
|
| [11] |
TSAY R S, ANDO T. Bayesian panel data analysis for exploring the impact of subprime financial crisis on the US stock market[J]. Computational statistics & data analysis, 2012, 56(11):3345-3365.
|
| [12] |
李红艳. 突发事件发展演化研究述评[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2017,26(2):212-216.
|
| [13] |
BRINK S A, DAVIDSON R A, TABUCCHI T H P. Strategies to reduce durations of post-earthquake water service interruptions in Los Angeles[J]. Structure and infrastructure engineering, 2012, 8(2):199-210.
|
| [14] |
HSU W K, CHIANG W L, CHEN C W. Earthquake risk assessment and optimal risk management strategies for Hi-Tech Fabs in Taiwan[J]. Natural hazards, 2013, 65(3):2063-2076.
|
| [15] |
李霖. 铁路突发事件应急资源优化布局与调配研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2016,
|
| [16] |
李群,代德军. 突发事件应急演练评估方法、技术及系统研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2016, 12(7): 49-54.
|
| [17] |
张欣,梅枝颖. 基于贝叶斯网的船舶溢油应急演练绩效评价[J]. 船海工程, 2018, 47(2): 104-108.
|
| [18] |
RASEKH A, VAFAEINEZHAD A R. Developing a GIS based decision support system for resource allocation in earthquake search and rescue operation[J]. Computational science and its applications, 2012, 7334: 275-285.
|
| [19] |
LI T, LI L. Music data mining: an introduction[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2011.
|
| [20] |
RAMESH R R, JON E, TED S, et al. Improving disaster management: the role of IT in mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery[M]. New York: National Academies Press, 2007.
|
| [21] |
何强. 大数据预测[J]. 中国统计, 2016(3):18-20.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |