 PDF(2459 KB)
PDF(2459 KB)


Information Visualization Analysis on the Research Hot Spots and Frontiers of International Corpus Linguistics
Yang Liu
Knowledge Management Forum ›› 2018, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (4) : 208-224.
 PDF(2459 KB)
PDF(2459 KB)
 PDF(2459 KB)
PDF(2459 KB)
Information Visualization Analysis on the Research Hot Spots and Frontiers of International Corpus Linguistics
[Purpose/significance] This paper aims at grasping the overall context and research findings of international corpus research in recent years, clarifying the hot spots and exploring the research frontiers in this field. [Method/process] It took the research papers published between 2005 and 2017 in Web of Science as data source, and made calculate analysis and knowledge domains map on these data through the softwares including BICOMB, Ucinet6 and CiteSpace from the following aspects:publication numbers and chronological distribution, source journals, research subjects, national and regional distribution, research institutions and cited literature. [Result/conclusion] It found that corpus study presents the characteristics of interdisciplinary and multi-angle, and it’s research objectsinvolve more languages and literature genre. Collocation and lexicography keep being important studies while special purpose language, academic English, gender, identity, metaphor and discourse analysis turn into new research hotspots, and the combination with construction grammar and cognitive linguistics are the research frontiers.
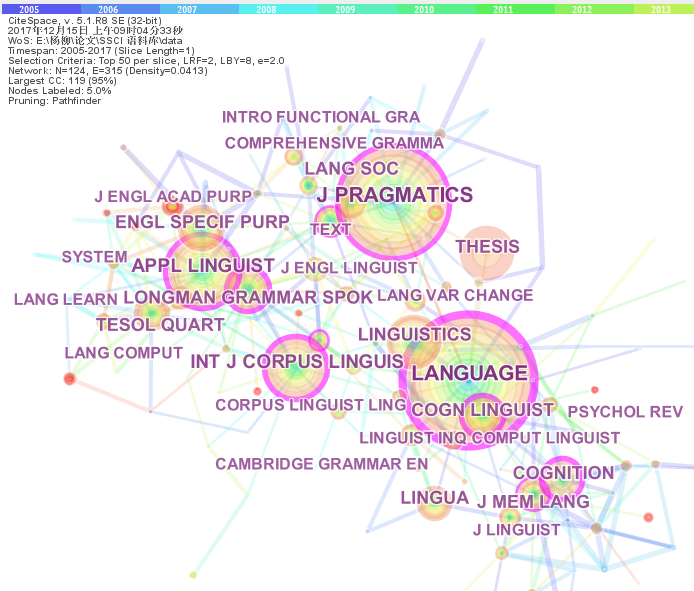
corpus / visualized analysis / BICOMB / Ucinet6 / CiteSpace
| [1] |
QUIRK R. Words at work: lectures on textual structure [M]. Singapore: NUS Press, 1986.
|
| [2] |
LEECH G. Corpora, the linguistics encyclopedia[M]. London:Routledge,1991.
|
| [3] |
McENERY T, XIAO R, TONO Y. Corpus-based language studies:an advanced resource book[M]. London: Routledge,2006.
|
| [4] |
SINCLAIR J. Corpus, concordance, collocation[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press,1991.
|
| [5] |
BAKER M. Corpus linguistics and translation studies: implications and applications [C] // BAKER M, FRANCIS G, TOGNINI-BONELLI E. Text and technology: in honour of John Sinclair. Philadelphia: John Benjamins,1993 :233-250.
|
| [6] |
ATKINS S, CLEAR J, OSTLER N. Corpus design criteria[J].Literary and linguistic computing, 1992, 7 , (1):1-16.
|
| [7] |
RENOUF A. Teaching corpus linguistics to teachers of English [C] //WICHMAN A, FLIGELSTONE S, McENERY T, et al. Teaching and language corpora. New York: Longman, 1997: 255-266.
|
| [8] |
桂诗春,杨惠中.中国学习者英语语料库[M].上海:上海外语教育出版社,2003.
|
| [9] |
王克非.语料库翻译学——新研究范式[J].中国外语,2006(3):8-9.
|
| [10] |
崔雷,刘伟,闫雷.文献数据库中书目信息共现挖掘系统的开发[J].现代图书情报技术,2008(8):70-75.
|
| [11] |
杨利军,吴智君.低被引文献对布拉德福定律的影响研究[J].情报理论与实践,2016,39(9):43-46.
|
| [12] |
褚旭,熊华军.2000年以来我国教育技术论文作者可视化分析——基于《中国电化教育》和《电化教育研究》载文[J].重庆高教研究,2015(6):100-108.
|
| [13] |
洪波.我国高等职业教育研究的知识图谱分析——基于1992-2016年核心期刊文献[J].职业技术教育,2017,38(6):45-50.
|
| [14] |
孙雨生,陈卫. 我国网格服务研究进展——基于CNKI(2003-2012)的文献计量与知识图谱分析[J]. 现代情报,2013,33(7):102-111.
|
| [15] |
廉同辉,余菜花,宗乾进.我国旅游网站的网络结构研究——基于社会网络分析法[J].旅游科学,2012,26(6):80-88.
|
| [16] |
WALTMAN L, van ECK N J, van LEEUWEN T N, et al. Towards a new crown indicator: an empirical analysis[J]. Scientometrics , 2011 87 (3) :467-481.
|
| [17] |
刘则渊,陈悦,侯海燕,等.科学知识图谱:方法与应用[M].北京:人民出版社,2008.
|
| [18] |
林德明,陈超美,刘则渊,等.共被引网络中介中心性的Zipf-Pareto分布研究[J].情报学报,2011, 30(1):76-82.
|
| [19] |
姜春林,胡志刚.《管理学报》2004-2009年载文计量分析[J].管理学报,2010,7(8):1137-1143.
|
| [20] |
索璠冰.基于CiteSpace和文献计量的国内云计算研究现状分析[J].图书情报导刊,2017,2(6):60-65.
|
| [21] |
李旭辉,李超,魏瑞斌,等.基于CSSCI的信息消费被引文献计量研究[J].图书馆工作与研究,2014(4):104-108.
|
| [22] |
GOLDBERG A. Constructions at work: the nature of generalization in language [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |