 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)


生成式人工智能技术的舆论动态与公众认知演化——基于ChatGPT的微博舆情研究
殷芝玲, 石晓雪, 黄晓, 卢新元
知识管理论坛 ›› 2025, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (4) : 335-347.
 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)
 PDF(2212 KB)
PDF(2212 KB)
生成式人工智能技术的舆论动态与公众认知演化——基于ChatGPT的微博舆情研究
Public Opinion Dynamics and Public Cognition Evolution of Generative Artificial Intelligence Technology——A Study on Weibo Public Opinion Based on ChatGPT
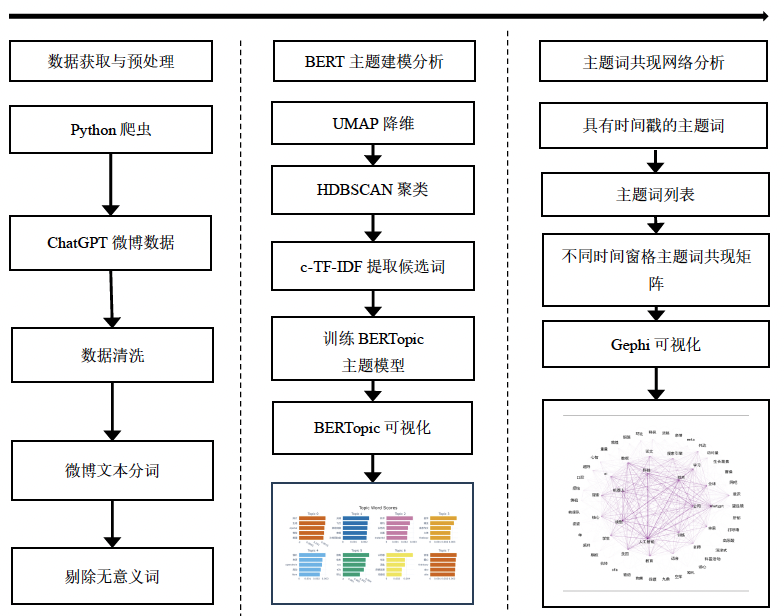
【目的/意义】 聚焦于生成式人工智能,特别是ChatGPT的公众舆情动态,旨在探讨这一技术的背景、意义及其社会影响,分析公众对其接受度和舆论演化过程,为相关技术应用和社会治理提供理论支持。 【方法/过程】 分析2023年1月至2024年9月间的221 564条与生成式人工智能相关的微博数据。通过BERTopic模型提取核心主题,并结合关键词共现网络分析不同时期的讨论热点和舆情演化。 【结果/结论】 识别科技产业、教育与机器人、健康医疗等八大主题,并揭示公众讨论的演化路径:初期关注技术创新与潜力,中期探讨场景应用(如教育、医疗与金融),后期则转向数据隐私、安全与社会伦理等问题。关键词分析表明,“人工智能”“技术”等术语贯穿全周期,而“隐私”“安全”等后期高频词反映公众对技术潜在风险的关注。研究结果可以为生成式人工智能技术的社会效应提供深入理解,并为技术优化与政策治理提供理论支持。
[Purpose/Significance] Focusing on the public opinion dynamics of generative artificial intelligence, especially ChatGPT, we aim to explore the background and significance of this technology and its social impact, analyze the public acceptance and public opinion evolution process, and provide theoretical support for the application of related technologies and social governance. [Method/Process] 221 564 microblog data related to generative AI between January 2023 and September 2024 were analyzed. By using the BERTopic model to extract the core themes and combining with keyword co-occurrence network analysis, we tracked the discussion hotspots and the evolution of public opinion in different time periods. [Result/Conclusion] This study identified eight major themes, including technology industry, education and robotics, and health care, and revealed the evolutionary path of public discussion: the initial phase focused on technological innovation and potential, the mid-term explored scenario applications such as education, health care, and finance, and the later stage turned to data privacy, security, and social ethics. Keyword analysis shows that terms such as "artificial intelligence" and "technology" run through the entire cycle, while high-frequency words such as "privacy" and "security" in the later period reflect the public's concern about the potential risks of technology. This study provides an in-depth understanding of the social effects of generative artificial intelligence technology and theoretical support for technology optimization and policy governance.
生成式人工智能 / ChatGPT / 舆情分析 / BERTopic / 主题分析
generative artificial intelligence / ChatGPT / public opinion analysis / BERTopic / topic analysis
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
王静静, 叶鹰.生成式AI及其GPT类技术应用对信息管理与传播的变革探析[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2023, 49(6): 41-50.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
吴江, 黄茜, 贺超城, 等.基于引爆点理论的人工智能生成内容微博网络舆情传播与演化分析[J]. 现代情报, 2023, 43(7): 145-161.
|
| [6] |
吴树芳, 郑依静, 朱杰.基于改进HK模型的社交用户观点演化预测研究[J]. 现代情报, 2024, 44(2): 142-151.
|
| [7] |
张连峰, 周红磊, 王丹, 等. 基于超网络理论的微博舆情关键节点挖掘[J]. 情报学报, 2019, 38(12): 1286-1296.
|
| [8] |
王旭娜, 张立凡. 基于超网络的重大突发事件公众认知演化与预警策略研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2024, 47(12): 183-194.
|
| [9] |
张鑫蕊, 张海涛, 栾宇, 等. 突发公共卫生事件的疫苗政策公众认知演化研究[J]. 情报科学, 2023, 41(8): 175-183.
|
| [10] |
吴孝灵, 刘小峰, 周晶. 基于公众认知与政府引导的邻避舆情演化模型[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2019, 39(11): 2865-2879.
|
| [11] |
杨欣谊, 王伟, 朱恒民. 基于时序共词网络的社交平台话题检测与演化研究[J]. 情报学报, 2023, 42(5): 585-597.
|
| [12] |
马晓悦, 薛鹏珍, 陈忆金, 等.社交媒体危机主题演化模型构建与趋势分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2021, 65(13): 77-86.
|
| [13] |
安璐, 杜廷尧, 李纲, 等. 突发公共卫生事件利益相关者在社交媒体中的关注点及演化模式[J]. 情报学报, 2018, 37(4): 394-405.
|
| [14] |
徐元, 毛进, 李纲. 面向突发事件应急管理的社交媒体多模态信息分析研究[J]. 情报学报, 2021, 40(11): 1150-1163.
|
| [15] |
郭宇, 张传洋, 张海涛, 等. 危机管理视角下突发事件舆情主题演化与治理分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(8): 113-121.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
陆伟, 马永强, 刘家伟, 等.数智赋能的科研创新——基于数智技术的创新辅助框架探析[J]. 情报学报, 2023, 42(9): 1009-1017.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
林鑫, 刘泽妃.ChatGPT生成综述的质量评测与应用策略[J]. 图书情报工作, 2024, 68(18): 32-40.
|
| [27] |
王俊, 谢青伶, 刘畅.日常生活情境下用户与生成式人工智能交互行为分析[J]. 图书情报知识, 2025, 42(2): 60-69, 93.
|
殷芝玲:数据收集与数据分析,撰写与修改论文;
石晓雪:数据收集,撰写论文;
黄晓:确定研究思路,修改论文与定稿;
卢新元:提供研究思路,修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |