 PDF(1368 KB)
PDF(1368 KB)


 PDF(1368 KB)
PDF(1368 KB)
 PDF(1368 KB)
PDF(1368 KB)
基于扎根理论的老年人网络沉迷行为与应对策略研究
Research on Internet Addiction Behaviors and Coping Strategies of the Seniors based on Grounded Theory
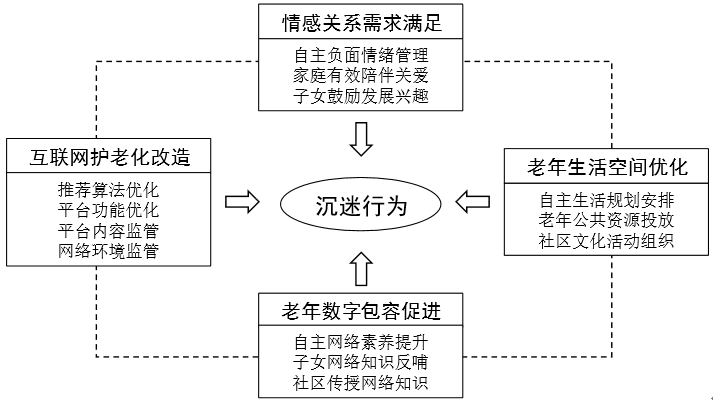
[目的/意义]互联网迅速渗透和适老化改造背景下,老年数字鸿沟和网络沉迷同时并存,老年人网络沉迷现象新兴,存在诸多潜在危害,亟待研究。[方法/过程]从网上爬取公开发表的老年人网络沉迷案例和专家分析意见,采用扎根理论质性分析方法,研究老年人网络沉迷的影响因素、行为特征、不良后果及应对策略,分别构建老年人网络沉迷的行为模型和应对模型。[结果/结论]个体因素(需求因素和能力因素)、情境因素(IT因素和生活因素)共同影响老年人网络沉迷行为的形成,需通过多元主体联动协同治理,采用情感关系需求满足、老年人数字包容促进、互联网护老化改造和老年人生活空间优化的策略进行应对,引导老年群体正确使用网络,共建老年友好型数字包容社会。
[Purpose/Significance] Under the background of the rapid penetration of the Internet and the aging transformation, the digital divide and Internet addiction of the seniors coexist, and the emerging phenomenon of Internet addiction of the seniors has many potential hazards, which need to be studied urgently. [Method/Process] This study crawled from the Internet published cases of the seniors’ Internet addiction and experts’ analysis opinions, adopted the grounded theory qualitative analysis method, studied the influential factors, behavioral characteristics, adverse consequences and coping strategies of the seniors’ Internet addiction, and constructed a behavioral model and a coping model of Internet addiction among the seniors. [Result/Conclusion] Individual factors (needs and abilities) and contextual factors (IT factors and living factors) jointly affect the formation of the seniors’ Internet addiction behaviors. It is necessary to adopt the multi-subject linkage and collaborative governance, adopt the strategies of satisfying the needs of emotional relationship, promoting the seniors’ digital inclusion, transforming the Internet care for the seniors and optimizing the seniors’ living space, so as to guide the seniors to use the Internet correctly and build an age-friendly digital inclusive society.
老年人 / 网络沉迷 / 沉迷行为 / 应对策略 / 扎根理论
seniors / Internet addiction / addiction behaviors / coping strategies / grounded theory
| [1] |
中国互联网络信息中心(CNNIC). 第51次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》[EB/OL].[2023-03-02]. https://www.cnnic.cn/NMediaFile/2023/0322/MAIN16794576367190GBA2HA1KQ.pdf.
|
| [2] |
趣头条, 澎湃新闻. 老年人网络生活报告:部分人或患网络孤独症,日在线超十小时[EB/OL].[2023-02-23]. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_9672026.
|
| [3] |
杜鹏, 谢立黎, 王飞. 积极老龄化视角下的老年人网络沉迷应对[J]. 晋阳学刊, 2022(3): 24-30.
|
| [4] |
段玉珍. 移动互联网时代“银发族”网络成瘾问题研究[J]. 卫星电视与宽带多媒体, 2020(2): 227-228,230.
|
| [5] |
CAPLAN S. A social skill account of problematic internet use[J]. Journal of communication, 2005, 55(4): 721-736.
|
| [6] |
DAVIS R. A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2001, 17(2): 187-195.
|
| [7] |
YOUNG K. Internet addiction - a new clinical phenomenon and its consequences[J]. American behavioral scientist, 2004, 48(4): 402-415.
|
| [8] |
Chen C, Zhang K Z K, Zhao S J. Examining the effects of perceived enjoyment and habit on smartphone addiction: the role of user type[C]//Proceedings of international conference on e-technologies. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 224-235.
|
| [9] |
刘勤学, 杨燕, 林悦, 等. 智能手机成瘾:概念、测量及影响因素[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2017, 25(1): 82-87.
|
| [10] |
周世杰, 唐志红, 彭阳. 网络成瘾青少年的网络相关行为特征[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2009, 17(2): 151-153,150.
|
| [11] |
雷雳. 青少年“网络成瘾”探析[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2010, 26(5): 554-560.
|
| [12] |
张锦涛, 刘勤学, 邓林园, 等. 青少年亲子关系与网络成瘾:孤独感的中介作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2011, 27(6): 641-647.
|
| [13] |
赵宝宝, 金灿灿, 邹泓. 青少年亲子关系、消极社会适应和网络成瘾的关系:一个有中介的调节作用[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2018, 34(3): 353-360.
|
| [14] |
方晓义, 刘璐, 邓林园, 等. 青少年网络成瘾的预防与干预研究[J]. 心理发展与教育, 2015, 31(1): 100-107.
|
| [15] |
邓验, 曾长秋. 青少年网络成瘾研究综述[J]. 湖南师范大学社会科学学报, 2012, 41(2): 89-92.
|
| [16] |
樊振佳, 骆卓昱. 高校学生"数字脱瘾"行为影响因素研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2022, 66(17): 106-115.
|
| [17] |
洪建中, 黄凤, 皮忠玲. 老年人网络使用与心理健康[J]. 华中师范大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2015, 54(2): 171-176.
|
| [18] |
许肇然, 胡安安, 黄丽华. 国内外老年人互联网使用行为研究述评[J]. 图书情报工作, 2017, 61(20): 140-148.
|
| [19] |
唐丹, 张琨, 亓心茹. 互联网使用对老年人社会网络及孤独感的影响:基于用途的分析[J]. 人口研究, 2022, 46(3): 88-101.
|
| [20] |
JIA Y, LIU T, YANG Y. The relationship between real-life social support and internet addiction among the elderly in China[J]. Frontiers in public health, 2022, 10: 981307.
|
| [21] |
YANG Y, LIU T, JIA Y. The impact of interaction with children on internet addiction in older adults: a moderated mediation model[J]. Frontiers in psychology, 2022, 13: 989942.
|
| [22] |
李晖. 国外激励理论与成功经验研究[J]. 求实, 2009(S1): 39-40.
|
| [23] |
宋志鹏, 张兆同. ERG理论研究[J]. 现代商业, 2009(3): 88-89.
|
| [24] |
曹娟, 安芹, 陈浩. ERG理论视角下老年人心理需求的质性研究[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2015, 23(2): 343-345,284.
|
| [25] |
唐艺. 人口老龄化视域下的老人身心需求研究与建议——基于ERG理论模型分析[J]. 南京艺术学院学报(美术与设计), 2020, 189(3): 157-164.
|
| [26] |
毛子骏, 刘子灵. 基于二维分析框架的中外养老政策文本比较研究[J]. 社会政策研究, 2021, 25(4): 35-48.
|
| [27] |
王文韬, 谢阳群, 占南. 基于ERG理论的数字原住民信息行为研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2015, 38(9): 42-46,7.
|
| [28] |
FREEMAN R E. Strategic management: a stakeholder approach[M]. Boston: Pitman Publishing Inc, 1984.
|
| [29] |
盛亚, 于卓灵. 论社会创新的利益相关者治理模式——从个体属性到网络属性[J]. 经济社会体制比较, 2018, 198(4): 184-191.
|
| [30] |
邓胜利, 王泽鑫. 利益相关者视角下基于健康码的社会治理关注研究[J]. 情报资料工作, 2022, 43(2): 36-45.
|
| [31] |
卢安文, 毛昕桐. 互联网信息服务业多元协同治理参与主体界定:一种新的分析框架[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2021(17): 68-81.
|
| [32] |
ARTHANAT S, VROMAN K G, LYSACK C, et al. Multi-stakeholder perspectives on information communication technology training for older adults: implications for teaching and learning[J]. Disability and rehabilitation: assistive technology, 2019, 14(5): 453-461.
|
| [33] |
PEEK S T M, WOUTERS E J, LUIJKX K G, et al. What it takes to successfully implement technology for aging in place: focus groups with stakeholders[J]. Journal of medical Internet research, 2016, 18(5): e5253.
|
| [34] |
张敬伟, 马东俊. 扎根理论研究法与管理学研究[J]. 现代管理科学, 2009(2): 115-117.
|
| [35] |
贾旭东, 衡量. 扎根理论的“丛林”、过往与进路[J]. 科研管理, 2020, 41(5): 151-163.
|
| [36] |
贾旭东, 衡量. 基于“扎根精神”的中国本土管理理论构建范式初探[J]. 管理学报, 2016, 13(3): 336-346.
|
| [37] |
陈向明. 扎根理论的思路和方法[J]. 教育研究与实验, 1999(4): 58-63,73.
|
| [38] |
SUDDABY R. From the editors: what grounded theory is not[J]. Academy of management journal, 2006, 49(4): 633-642.
|
| [39] |
杜晓君, 刘赫. 基于扎根理论的中国企业海外并购关键风险的识别研究[J]. 管理评论, 2012, 24(4): 18-27.
|
| [40] |
GUEST G, BUNCE A, JOHNSON L. How many interviews are enough? an experiment with data saturation and variability[J]. Field methods, 2006, 18(1): 59-82.
|
| [41] |
黄炜, 王珊珊, 戴辛宇. 直播电商用户购买行为影响因素研究[J]. 知识管理论坛, 2021, 6(6): 315-326.
|
| [42] |
孙晓军, 赵竞, 周宗奎, 等. 时间管理倾向与病理性网络使用的关系:网络自我控制的中介作用[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2015, 13(3): 410-413.
|
| [43] |
武文颖, 朱金德. 网络适老化的伦理反思与规制[J]. 学术交流, 2021(10): 115-129.
|
| [44] |
左美云. 智慧养老:内涵与模式[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社, 2018.
|
| [45] |
Kemperman A, van den Berg P, Weijs-Perrée M, et al. Loneliness of older adults: social network and the living environment[J]. International journal of environmental research and public health, 2019, 16(3): 406.
|
陈若瑶:进行研究设计、资料收集、资料编码和论文撰写;
左美云:确定研究选题,进行研究设计、资料编码和论文修改。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |