 PDF(3010 KB)
PDF(3010 KB)


 PDF(3010 KB)
PDF(3010 KB)
 PDF(3010 KB)
PDF(3010 KB)
考虑知识创新与传播意愿的企业间知识传播模型
Inter-Firm Knowledge Dissemination Model That Considers Knowledge Innovation and the Willingness to Disseminate Knowledge
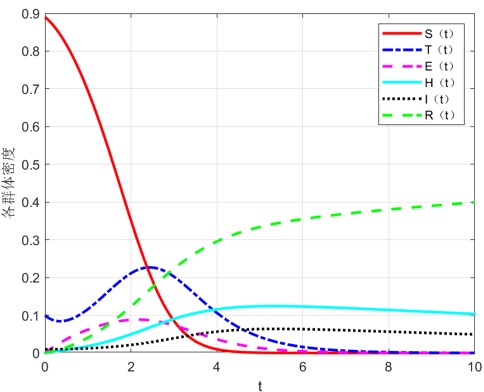
[目的/意义]知识经济时代,企业知识被认为是企业发展的主要驱动力,如何找到知识传播规律,进行有效的知识传播成为学者们日益关心的问题。[方法/过程]在经典的传染病模型SEIR模型基础上,将企业分为知识创新型企业与一般知识未知企业,在考虑知识创新型企业能够进行知识创新的基础上,结合企业知识传播意愿对企业知识传播的影响,构建考虑企业知识传播意愿的B-STEHIR模型,并给出该模型的平均场方程。同时,通过下一代矩阵法求解基本再生数,使用Matlab2020a对该模型进行仿真模拟。[结果/结论]在创新型企业的知识创新引领下,传播意愿这一因素在企业知识传播过程中起到重要作用,对比不考虑传播意愿的知识传播模型,在考虑传播意愿的知识传播模型中知识传播得更慢;创新知识传播意愿越强会使一般知识传播越慢,企业与政府可采取各种办法促进企业知识有效传播。
[Purpose/Significance] In the era of knowledge economy, enterprise knowledge is considered to be the main driving force for the development of enterprises, how to find the law of knowledge dissemination and carry out effective knowledge dissemination has become an increasing concern of scholars. [Method/Process] On the basis of the classic infectious disease model SEIR model, enterprises are divided into knowledge innovation enterprises and general knowledge unknown enterprises. On the basis of considering that knowledge innovation enterprises can carry out knowledge innovation, combined with the influence of enterprise knowledge dissemination willingness on enterprise knowledge dissemination, a B-STEHIR model considering the willingness of enterprise knowledge dissemination under the guidance of knowledge innovation of innovative enterprises is constructed, and the average field equation of the model is proposed. At the same time, the basic regeneration number is solved by the next-generation matrix method, and the model is simulated using Matlab2020a. [Result/Conclusion] The results show that under the guidance of knowledge innovation of innovative enterprises, the factor of willingness to disseminate plays an important role in the process of enterprise knowledge dissemination, and knowledge spreads more slowly in the knowledge dissemination model that considers the willingness to spread compared with the knowledge dissemination model that does not consider the willingness to spread The stronger the willingness to disseminate innovative knowledge, the slower the dissemination of general knowledge, and enterprises and governments can take various measures to promote the effective dissemination of corporate knowledge.
企业知识 / 知识传播 / SEIR模型 / 传播意愿 / B-STEHIR模型
corporate knowledge / knowledge dissemination / SEIR model / willingness to disseminate / B-STEHIR model
| [1] |
WANG H, WANG J, DING L, et al. Knowledge transmission model with consideration of self-learning mechanism in complex networks[J]. Applied mathematics and computation, 2017, 304:83-92.
|
| [2] |
BABCOCK P. Shedding light on knowledge management[J].HR magazine,2004,49 (5): 46-50.
|
| [3] |
BOCK G W,KIM Y G. Breaking the myths of rewards: an exploratory study of attitudes about knowledge sharing[J],Information resources management journal,2002,15 (2) : 14-21.
|
| [4] |
PINCH S, HENRY N. Paul Krugman’s geographical economics, industrial clustering and the British motor sport industry[J]. Regional studies, 1999, 33(9): 815-827.
|
| [5] |
FERNANDES K J, RAJA V. A practical knowledge transfer system: a case study[J]. Work study, 2002, 51(3):140-148.
|
| [6] |
SYED O, ROWLAND F. Knowledge management in a public organization: a study on the relationship between organizational elements and the performance of knowledge transfer[J]. Journal of knowledge management, 2004, 8(2):95-111.
|
| [7] |
GOH S C. Managing effective knowledge transfer: an integrative framework and some practice implications[J]. Journal of knowledge management, 2002, 6(1):23-30.
|
| [8] |
KERMACK W O, MCKENDRICK A G A. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: mathematical physical and engineering sciences, 1927, 115(772):700-721.
|
| [9] |
GOFFMAN W. Mathematical approach to the spread of scientific ideas[J]. Nature, 1966, 212(5061):449-452.
|
| [10] |
LIAO S G, YI S P. Modeling and analyzing knowledge transmission process considering free-riding behavior of knowledge acquisition: a waterborne disease approach[J]. Physica A: statistical mechanics and its applications, 2021,569(1):0378-4371.
|
| [11] |
WANG H, WANG J, DING L, et al. Knowledge transmission model with consideration of self-learning mechanism in complex networks[J]. Applied mathematics and computation, 2017, 83(92): 0096-3003.
|
| [12] |
LIAO S G, YI S P. Modeling and analysis knowledge transmission process in complex networks by considering internalization mechanism[J]. Chaos solitons & fractals, 2021, 143(1): 110-593.
|
| [13] |
YUE Z, XU H, YUAN G, et al. Modeling study of knowledge diffusion in scientific collaboration networks based on differential dynamics: a case study in graphene field[J]. Physica A: statistical mechanics and its applications, 2019, 524:375-391.
|
| [14] |
胡绪华, 陈丽珍, 吕魁. 基于传染病模型的集群内异质企业间知识传播机理分析与仿真[J]. 运筹与管理, 2015, 24(3): 248-257.
|
| [15] |
谭建. 基于小世界网络的企业集群知识传播模型[J]. 科技与经济, 2012, 25(6):11-15.
|
| [16] |
綦良群,吴佳莹,王智慧.先进制造企业协同创新网络知识共享的演化博弈[J/OL].计算机集成制造系统,2022:1-23[2022-04-15].
|
| [17] |
马宇彤, 胡平. 考虑“关键用户”影响力及“热点问题”识别的改进SEIR知识传播模型[J]. 预测, 2021, 40(5):48-55.
|
| [18] |
马永红, 刘海礁, 柳清. 产业集群协同创新知识共享策略的微分博弈研究[J]. 运筹与管理, 2020, 29(9):82-88.
|
| [19] |
姚凯, 汤建影. 雇佣关系、组织公平与知识共享意愿:基于中国企业的实证研究[J]. 复旦学报:自然科学版, 2016(1):8-17,27.
|
| [20] |
唐厚兴. 市场竞争结构对虚拟联盟内知识领先企业共享意愿的影响[J]. 科技管理研究, 2016, 36(22):150-156.
|
| [21] |
UDIN A, RADVAN D, ISALMAN I. Transactional leadership and innovative work behavior: testing the mediation role of knowledge sharing in distribution market[J]. Journal of distribution science,2022, 20(1):41-53.
|
| [22] |
AZEEM M, AHMED M, HAIDER S, et al. Expanding competitive advantage through organizational culture, knowledge sharing and organizational innovation[J]. Technology in society, 2021, 66(7):101635.
|
| [23] |
CHUMG H F, SEATON J, COOKE L, et al. Factors affecting employees' knowledge-sharing behaviour in the virtual organisation from the perspectives of well-being and organisational behaviour[J]Computers in human behavior,2016,64:432-448
|
| [24] |
AJZEN I, FISHBEIN M. Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior[M]. Englewood Cliffs:Englewood cliffs, 1980.
|
| [25] |
肖峰.知识传播的现代方式及其特征探析[J].武汉科技大学学报(社会科学版),2021,23(1):85-91.
|
| [26] |
齐廉文,吴洁,庄蕾,等.生态视域下创业生态系统异质企业间知识转移机理研究[J].复杂系统与复杂性科学,2021,18(4):74-83.
|
| [27] |
李常洪,张曦.组织中情绪氛围对隐性知识共享的影响——基于多agent的仿真研究[J].情报理论与实践,2016,39(9):77-81.
|
| [28] |
DIEKMANN O, Heesterbeek J, Metz J. On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio R0 in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations[J]. Journal of mathematical biology, 1990, 28(4):365-382.
|
| [29] |
van den Driessche P, Watmough J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission[J]. Mathematical biosciences, 2002, 180(1/2):29-48.
|
| [30] |
AL-DARABSAH I, YUAN Y. A time-delayed epidemic model for Ebola disease transmission[J]. Applied mathematics and computation, 2016, 290: 307-325.
|
连卓毅:确定论文主题,撰写论文;
王筱莉:指导研究思路,修改论文;
张静:修改论文;
钱梦迪:修改论文;
陈淑琴:修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |