 PDF(1291 KB)
PDF(1291 KB)


 PDF(1291 KB)
PDF(1291 KB)
 PDF(1291 KB)
PDF(1291 KB)
老年人对增强现实旅游场景的接受行为研究:基于TRI-UTAUT2模型
Acceptance Behavior of the Elderly in Augmented Reality Tourism Scenes: Based on TRI/UTAUT2 Model
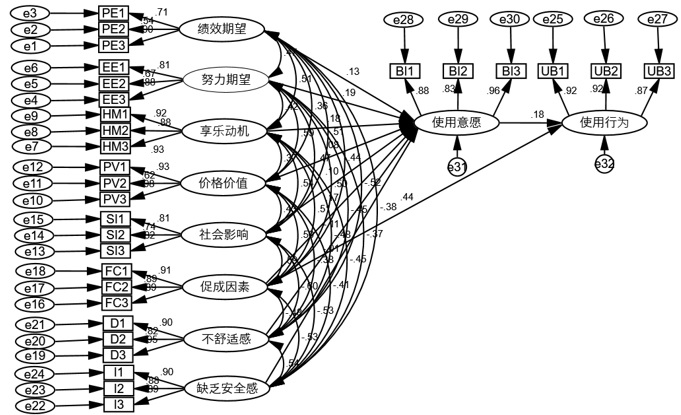
[目的/意义] 针对老年群体,探究其对于新技术应用的接受行为并发现规律。[方法/过程] 基于整合科技接受模型(UTAUT2)和技术准备度(TRI)理论,构建老年群体对增强现实旅游场景的接受行为模型,提出研究假设,并采用问卷调查的方式收集数据,运用结构方程模型、SPSS和AMOS软件验证假设,对老年人群体中增强现实旅游场景的接受行为的影响因素进行研究。[结果/结论] 老年群体中促成因素不能显著影响使用意愿但显著影响使用行为;老年群体中绩效期望、努力期望、社会影响、价格价值和不舒适感是使用意愿的主要前因变量;老年群体中使用意愿是接受行为的显著影响因素,享乐动机和缺乏安全感对其接受意愿并无显著影响。
[Purpose/Significance] This paper aims to explore the acceptance behavior of the elderly for the application of new technologies and find out its regular pattern.[Method/Process] Based on the UTAUT2 and TRI, this paper constructed a behavior model of the elderly for the use of augmented reality tourism scenarios, put forward research hypotheses, collected data by means of questionnaire survey, and verified hypotheses by using structural equation model, SPSS and AMOS software, to verify the influencing factors of augmented reality tourism scene acceptance behavior among the elderly. [Result/Conclusion] The results show that: the contributing factors in the elderly group cannot significantly affect the use intention, but significantly affect the use behavior. Performance expectation, effort expectation, social impact, price value and discomfort are the main antecedents of use intention in the elderly group. The use intention of the elderly is a significant influencing factor of use behavior, and hedonic motivation and lack of security have no significant impact on their use intention.
老年人 / 增强现实 / 游客使用行为 / 技术准备度 / 整合科技接受模型
the elderly / augmented reality / tourist use behavior / TRI / UTAUT
| [1] |
中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2012[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2013.
|
| [2] |
任明丽, 李群绩, 何建民. 身体状况还是积极心态?——关于中国老年家庭出游限制因素的经验分析[J]. 旅游学刊, 2018, 33 (5): 26-43.
|
| [3] |
KIM H, WOO E, UYSAL M. Tourism experience and quality of life among elderly tourists[J]. Tourism management, 2015, 46(1): 465-476.
|
| [4] |
MOSCARDO G, GREEN D. Age and activity participation on the great barrier reef[J]. Tourism recreation research, 1999, 24 (1): 57-68.
|
| [5] |
马桂顺,龙江智,李恒云.不同特质银发族旅游目的地选择影响因素差异 [J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(12): 2185-2196.
|
| [6] |
姚延波,侯平平.近十年国外老年旅游研究述评与展望[J]. 旅游论坛, 2019, 12(2): 82-94.
|
| [7] |
HJALAGER A M.A review of innovation research in tourism[J]. Tourism management,2010,31( 1) : 1-12.
|
| [8] |
AZUMA R,BILLINGHURST M,KLINKER G.Special section on mobile augmented reality[J].Computers & graphics,2011,35(4) : vii-viii.
|
| [9] |
CHUNG N,HAN H,JOUN Y.Tourists' intention to visit a destination: the role of augmented reality(AR) application for a heritage site[J].Computers in human behavior,2015,50(2) : 588-599.
|
| [10] |
苏文成,卢章平,王正兴.维护长者选择的尊严:老年群体数字技术应用自主性行为概念模型 [J]. 图书馆论坛,2021,41(8):86-95.
|
| [11] |
钱宇星,李浩,倪珍妮,等.论坛式网络信息服务适老化困境与应对——以“银龄网”关停为例 [J]. 图书情报知识,2021(2):68-78.
|
| [12] |
WU W Q, WU Y J, WANG H X. Perceived city smartness level and technical information transparency: the acceptance intention of health information technology during a lockdown[J]. Computers in human behavior,2021,122(9):106840.
|
| [13] |
SCHEPERS J,WETZELS M. A meta-analysis of the technology acceptance model: investigating subjective norm and moderation effects[J].Information & management,2007,44 (1) : 90-103.
|
| [14] |
OH S H,KIM Y M,LEE C W,et al.Consumer adoption of virtual stores in Korea: focusing on the role of trust and playfulness[J].Psychology & marketing,2009,26(7) : 652-668.
|
| [15] |
PARASURAMAN A.Technology Readiness Index (TRI) : a multiple-item scale to measure readiness to embrace new technologies[J].Journal of service research,2000,2(4) : 307-320.
|
| [16] |
周波,周玲强,吴茂英.智慧旅游背景下增强现实对游客旅游意向影响研究——一个基于TAM的改进模型[J].商业经济与管理,2017(2):71-79.
|
| [17] |
LIN C H, SHIH H Y, SHER P J. Integrating technology readiness into technology acceptance: the TRAM model [J]. Psychology & marketing, 2007, 24 (7): 641-657.
|
| [18] |
VENKATESH V, THONG J Y L, XU X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology[J]. MIS quarterly. 2012, 36(1): 157-178.
|
| [19] |
VENKATESH V, MORRIS M G, DAVIS G B, et al. User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view [J]. MIS quarterly, 2003, 27(3): 425-478.
|
| [20] |
吕红敏. 基于UTAUT2模型的无人超市消费者使用意愿影响因素研究[D].北京:北京邮电大学,2020.
|
| [21] |
YUAN S, MA W, KANTHAWALA S, et al. Keep using my health apps: discover users' perception of health and fitness apps with the UTAUT2 model[J]. Telemedicine journal and e-health, 2015, 21(9): 735.
|
| [22] |
BAPTISTA G, OLIVEIRA T. Understanding mobile banking: the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology combined with cultural moderators[J]. Computers in human behavior, 2015, 50(9): 418-430.
|
| [23] |
NYSVEEN H, PEDERSEN P E, THORBJ RNSEN H. Intentions to use mobile services: antecedents and cross-service comparisons[J]. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 2005 33(3); 330-346 .
|
| [24] |
KIJSANAYOTIN B, PANNARUNOTHAI S, SPEEDIE S M. Factor’s influencing health information technology adoption in Thailand’s community health centers: applying the UTAUT model[J]. International journal of medical informatics, 2009, 78(6): 404-416.
|
| [25] |
AFSHAN S, SHARIF A. Acceptance of mobile banking framework in Pakistan[J]. Telematics and informatics, 2016, 33(2): 370-387.
|
| [26] |
王雪彬, 周建华, 易法敏. O2O模式下消费者网购农产品的影响因素研究[J]. 南方农村, 2016(6): 15-21, 39.
|
| [27] |
BROWN S A, VENKATESH V. Model of adoption of technology in households: a baseline model test and extension incorporating household life cycle[J]. Mis quarterly, 2006, 22(4): 205-218.
|
| [28] |
张敏, 林盛. 大学生对即时通讯软件使用行为的影响因素研究[J]. 上海管理科学, 2016, 38(4): 66-70.
|
| [29] |
TSAI H S, LAROSE R. Broadband Internet adoption and utilization in the inner city: a comparison of competing theories[J]. Computers in human behavior. 2015, 51(10), Part A: 344-355.
|
| [30] |
马静, 董占鹏. 可穿戴设备消费者接受度实证研究[J]. 未来与发展, 2015, 39(9): 37-41.
|
| [31] |
闫晨晖. 基于UTAUT2的无人零售消费者接受行为研究[D].郑州:河南大学,2019.
|
| [32] |
OH J C, YOON S J, CHUNG N. The role of technology readiness in consumers’adoption of mobile internet services between South Korea and China[J]. International journal of mobile communications, 2014, 12(3): 229-248.
|
| [33] |
COSTA F, BENTO A D. Factor from technology readiness index (TRI) as antecedents of technology acceptance model (TAM) [J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 2008, 12(2): 429-456.
|
| [34] |
KWON H S, CHIDAMBARAM L. A test of the technology acceptance model: the case of cellular telephone adoption[C]// SPRAGUE R H J. Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences. Maui: IEEE, 2000: 87-96.
|
| [35] |
胡田, 郭英之. 旅游消费者在线购买旅游产品的信任度、满意度及忠诚度研究[J]. 旅游科学, 2014, 28(6): 40-50.
|
| [36] |
AJZEN I. The theory of planned behavior[J]. Organizational behavior & human decision processes, 1991, 50(2): 179–211.
|
李骄阳:收集与处理数据,撰写及修改论文;
樊振佳:确定论文选题框架,提出修改意见,完善研究内容并修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |