 PDF(1255 KB)
PDF(1255 KB)


 PDF(1255 KB)
PDF(1255 KB)
 PDF(1255 KB)
PDF(1255 KB)
基于用户特征的电费回收分析及策略——电力知识化转型工程实践
Analysis and Strategy of Electricity Charge Recovery Based on User Characteristics ——Engineering Practice of Power Knowledge Transformation
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,

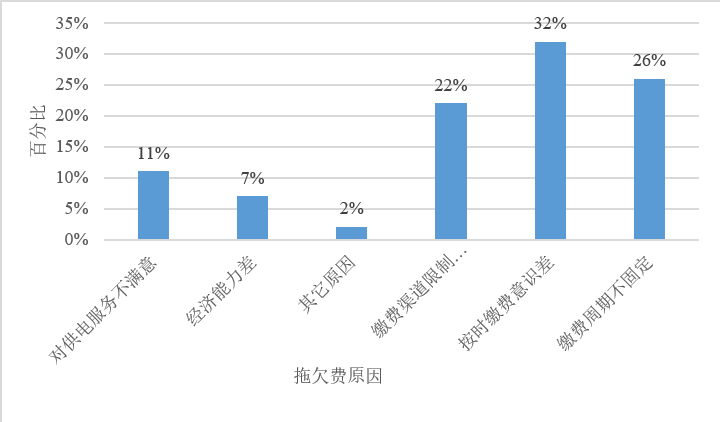
[目的/意义]随着知识管理相关理论的发展,各相关工业部门特别是完成了信息化的工业部门也面临着越来越紧迫的知识化转型。在知识化转型过程中除知识管理的相关理论外,也需要提炼出知识管理相关工具体系。[方法/过程]主要研究知识管理相关工具在电力行业市场营销领域中的应用,从电力业务人员日常接触的数据中萃取影响缴费用户的特征因素,并形成与用户缴费欠费习惯相关的关键知识,为业务人员未来工作进行指导。首先,从电力系统中采集甘肃省内近10万户的用电及缴费数据,并整理出由问卷调查获得的数据;其次,采用主成分分析及回归方法构造用户按时缴费模型;最后,根据模型分析获得促使用户按时缴费的因素,提出针对性的营销策略,以降低电费拖欠率并降低电费回收成本。[结果/结论]通过分析,找到用户履约能力、客户满意度及征缴频率等关键因素,较好地实现电力知识化转型。
[Purpose/significance] With the development of knowledge management related theories, all relevant industrial sectors, especially those that have completed informatization, are also facing an increasingly urgent transformation of knowledge. In the process of knowledge transformation, in addition to the related theories of knowledge management, knowledge management related tool systems need to be refined.[Method/process] This paper took the power industry as an example to explore the application of knowledge management related tools in power marketing. Experienced power system practitioners can use their tacit knowledge to analyze key factors in the power system marketing process. This paper attempted to use explicit knowledge management tools to make tacit knowledge explicit. This paper studied the factors that prompt users to pay on time, proposed targeted marketing strategies, reduced the arrears rate, improves the method of electricity bill recovery, and reduces the cost of electricity bill recovery. This paper used principal component analysis and regression methods to construct a user's on-time payment model based on the electricity consumption and payment data of nearly 100000 households in Gansu Province and part of the data from the questionnaire survey. [Result/Conclusion] Through analysis, the key factors such as paying attention to user performance, customer satisfaction and collection frequency were found, and the explicit expression of tacit knowledge was better achieved.
knowledge of power system / data intelligence / power marketing / user characteristics
| [1] |
潘绍立,梁经纬.电力营销管理现状及前瞻性分析[J].现代商贸工业,2018,39(36):47-48.
|
| [2] |
周晖,王毅,王玮,等.基于Logistic回归模型的电力客户欠费违约概率的预测[J].电网技术,2007(17):85-88.
|
| [3] |
葛洲,余英,郑莎莎,等.窃电现象对供电系统的影响及反窃电系统[J].科技创业月刊,2012,25(12):198-199,201.
|
| [4] |
申纪,吟李.企业拖欠电费的症结何在──关于拖欠电费的法律思考[J].农电管理,1997(2):26.
|
| [5] |
黄文思,郝悍勇,李金湖,等.基于决策树算法的电力客户欠费风险预测[J].电力信息与通信技术,2016,14(1):19-22.
|
| [6] |
张禄,潘鸣宇,田贺平,等.基于数据挖掘技术的电力客户欠费风险预警研究[J]计算机科学与探索,2017(11):588-594.
|
| [7] |
李宗隆,江京金,晏偌峰,等.基于电费风险确定权重的评价模型方法分析研究[J]计算机科学与探索,2017(11):192-194,396.
|
| [8] |
王彬,何光宇,陈颖,等.智能电网评估指标体系中电力用户需求指标集的构建[J].电网技术,2012,36(6):21-26.
|
| [9] |
潘俊涛,李泰霖,李金瑾,等.基于层次分析法和专家经验的预付费电能表用户欠费风险评估策略[J].广西电力,2016,39(4):15-17,21.
|
| [10] |
吴漾,朱洲.基于特征选择改进LR-Bagging算法的电力欠费风险居民客户预测[J].电子产品世界,2017,24(4):70-75.
|
| [11] |
陈羽中,郭松荣,陈宏,等.基于并行分类算法的电力客户欠费预警[J].计算机应用,2016,36(6):1757-1761.
|
| [12] |
陈佩莉,钱毅慧,潘勤,等.基于交费大数据的电力用户欠费风险等级研究[J].自动化技术与应用,2019,38(1):50-53.
|
| [13] |
夏国明,谢华.用电营业管理[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社,2004.
|
| [14] |
张春城.全过程防范,破解电费回收难题[J].国家电网,2006(2):49-51.
|
| [15] |
杜建实.规避电费回收风险 推行“购电制”[J].华北电业,2007(5):54-55.
|
| [16] |
解召辉.浅谈电费风险预警管理[J].农村电工,2014,22(6):10-11.
|
| [17] |
张志华.浅析降低专变电费现金收取比例[J].科技视界,2014(29):271.
|
江 元:文献查阅及论文写作;
杨 波:数据采集及整理,论文部分内容写作;
王 麒:数据挖掘及分析;
赵东来:修改论文;
武 悦:设计论文整体框架,论文校稿。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |