 PDF(1206 KB)
PDF(1206 KB)


 PDF(1206 KB)
PDF(1206 KB)
 PDF(1206 KB)
PDF(1206 KB)
日常生活场景中的个人智能连接服务研究
Research on Personal Smart Connection Service in Everyday Life Scenarios
[目的/意义]日常生活场景中丰富多样的APP和智能硬件为个人带来了新的连接体验,以自动化、主动化和个性化为特征的个人智能连接服务分析,有助于信息服务的新场景融入与手段丰富化。[方法/过程]首先,归纳日常生活场景的主要类型,剖析场景内涵与要素、场景要素之间的连接及数据的连通;其次,在场景要素连接的基础上,讨论场景之间的切换;再次,提出以“IF-THEN”逻辑构筑个人智能连接,以“触发器-动作”编程作为服务实现手段,分析典型的服务应用。[结果/结论]提出一种基于“IF-THEN”逻辑的“触发器-动作”编程式个人智能连接服务设计方法,为日常生活场景中的个性化信息服务设计提供参考。
[Purpose/significance] From the perspective of everyday life scenario, this paper studies the way App and hardware provide smart information service for users with automation, initiative and personalization. [Method/process] First, this paper analyzed the significance and elements of the context and classified the main personal context types according to user’s everyday life scenarios. Then, it analyzed the connections between user, APP, and smart hardware, and the data flow in the context and studied the design of "IF-THEN" logic rules and the corresponding practice of trigger-action programming. Finally, this paper compared typical examples of smart services based on trigger-action programming. [Result/Conclusion] This paper proposes a flow design based on "IF-THEN" logic and trigger-action programming for smart information service in personal everyday life, which could create the basis of the theory and implementation of service design for the integration of new scenes.
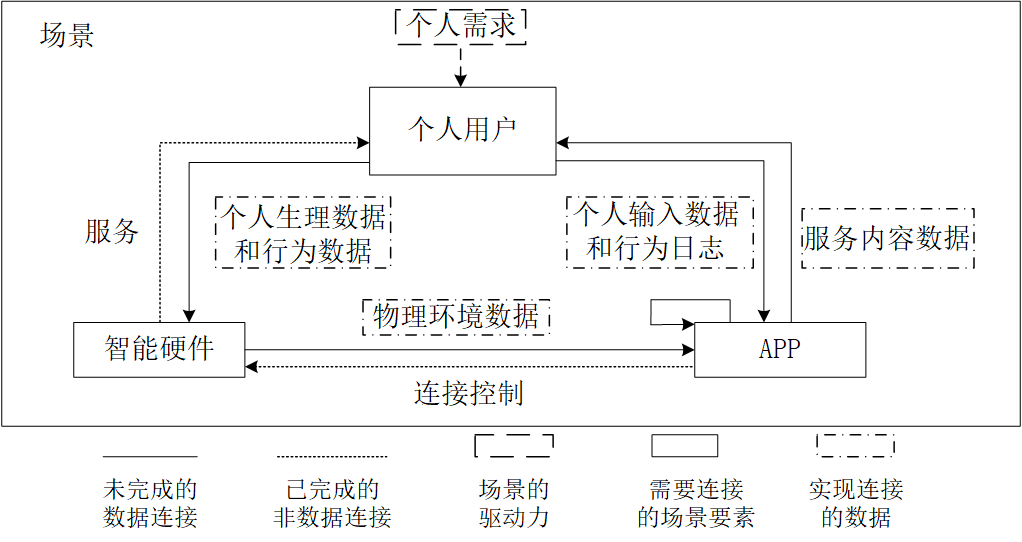
everyday life scenario / connections / IF-THEN / smart service
| [1] |
SAVOLAINEN R. Everyday life information seeking: approaching information seeking in the context of “way of life” [J]. Library & information science research, 1995, 17(3):259-294
|
| [2] |
吴丹, 梁少博. 多设备环境下网络信息搜索行为研究综述[J]. 中国图书馆学报, 2015, 41(6):109-127
|
| [3] |
BAWDEN D. The turn: integration of information seeking and information retrieval in context[J]. Journal of documentation, 2005, 43(2):821-822
|
| [4] |
场景实验室. 2018年场景白皮书[EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. http://www.199it.com/archives/734109.html
|
| [5] |
刘强, 崔莉, 陈海明. 物联网关键技术与应用[J]. 计算机科学, 2010, 37(6):1-4
|
| [6] |
周晓杰, 刘海昕, 张春杨. 我国图书馆嵌入式服务研究述评[J]. 图书馆学研究, 2012(12):19-22
|
| [7] |
CHEN G, KOTZ D. A survey of context-aware mobile computing research[R]. Technical Report TR2000-381. Hanover: Dept. of Computer Science, Dartmouth College, 2000
|
| [8] |
KO H, RAMOS C. A survey of context classification for intelligent systems research for Ambient Intelligence[C]//Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS), 2010 International Conference on. Washington: IEEE, 2010: 746-751
|
| [9] |
吴声. 场景革命[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社, 2015:197-220
|
| [10] |
中国产业信息网. 2016年中国人工智能应用领域分析[EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. http://www.chyxx.com/industry/201612/482350.html
|
| [11] |
中国互联网络信息中心. 第44次中国互联网络发展状况统计报告[EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. http://www.cnnic.net.cn/hlwfzyj/hlwxzbg/hlwtjbg/201908/P020190830356787490958.pdf
|
| [12] |
肖永英, 何兰满. 国外日常生活信息查询行为研究进展(2001-2010)[J]. 图书情报工作, 2012, 56(5):112-118
|
| [13] |
BATES M J. The design of browsing and berrypicking techniques for the online search interface[J]. Online review, 1989, 13(5): 407-424
|
| [14] |
DEY A K, SOHN T, STRENG S, et al. iCAP: interactive prototyping of context-aware applications[C]// International conference on pervasive computing. Berlin: Springer, 2006:254-271
|
| [15] |
HOY M B. If this then that: an introduction to automated task services[J]. Medical reference services quarterly, 2015, 34(1): 98-103
|
| [16] |
GHIANI G, MANCA M, PATERNO F, et al. Individualization of context-dependent applications through trigger-action rules[J]. ACM transactions on computer-human interaction, 2017, 24(2):1-33
|
| [17] |
HUANG J, CAKMAK M. Supporting mental model accuracy in trigger-action programming[C]// Proceedings of the 2015 ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing. New York: ACM, 2015: 215-225
|
| [18] |
UR B, MCMANUS E, HO M P Y, et al. Practical trigger-action programming in the smart home[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems. New York: ACM, 2014: 803-812
|
| [19] |
Wikipedia. End-user development [EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/End-user_development
|
| [20] |
CORNO F, DE RUSSIS L, ROFFARELLO A M. A semantic web approach to simplifying trigger-action programming in the IoT[J]. Computer, 2017, 50(11): 18-24
|
| [21] |
DESOLDA G, ARDITO C, MATERA M. Empowering end users to customize their smart environments: model, composition paradigms, and domain-specific tools[J]. ACM transactions on computer-human interaction, 2017, 24(2): 12
|
| [22] |
PARECKI A. OAuth 2.0 [EB/OL]. [2020-01-26]. https://oauth.net/2/
|
| [23] |
O'REILLY T. Pipes and filters for the Internet [EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. http://radar.oreilly.com/2007/02/pipes-and-filters-for-the-inte.html
|
| [24] |
Zapier. What is Zapier? [EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. https://zapier.com/learn/getting-started-guide/what-is-zapier/
|
| [25] |
WEARE K. Microsoft flow reaches general availability[EB/OL].[2019-11-11]. https://www.infoq.com/news/2016/11/microsoft-flow-ga
|
| [26] |
Microsoft Flow.自动化进程+任务[EB/OL].[2019-11-11]. https://flow.microsoft.com/zh-cn/
|
| [27] |
Google Play. The winners of the 2017 Google Play Awards [EB/OL]. [2019-11-11]. https://blog.google/products/google-play/winners-2017-google-play-awards-are/
|
| [28] |
RAHMATI A, FERNANDES E, JUNG J, et al. IFTTT vs. Zapier: a comparative study of trigger-action programming frameworks[J/OL]. arXiv:1709.02788, 2017[2020-01-20]. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017arXiv170902788R
|
郭 露:负责资料收集与分析,论文初稿撰写;
范 炜:负责论文选题,论文框架设计,论文指导与修改。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |