 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)


 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)
 PDF(1823 KB)
PDF(1823 KB)
老年人智慧养老技术持续使用意愿影响因素的元分析
Influencing Factors of Smart Senior Technology Continuance Intention Based on Meta Analysis
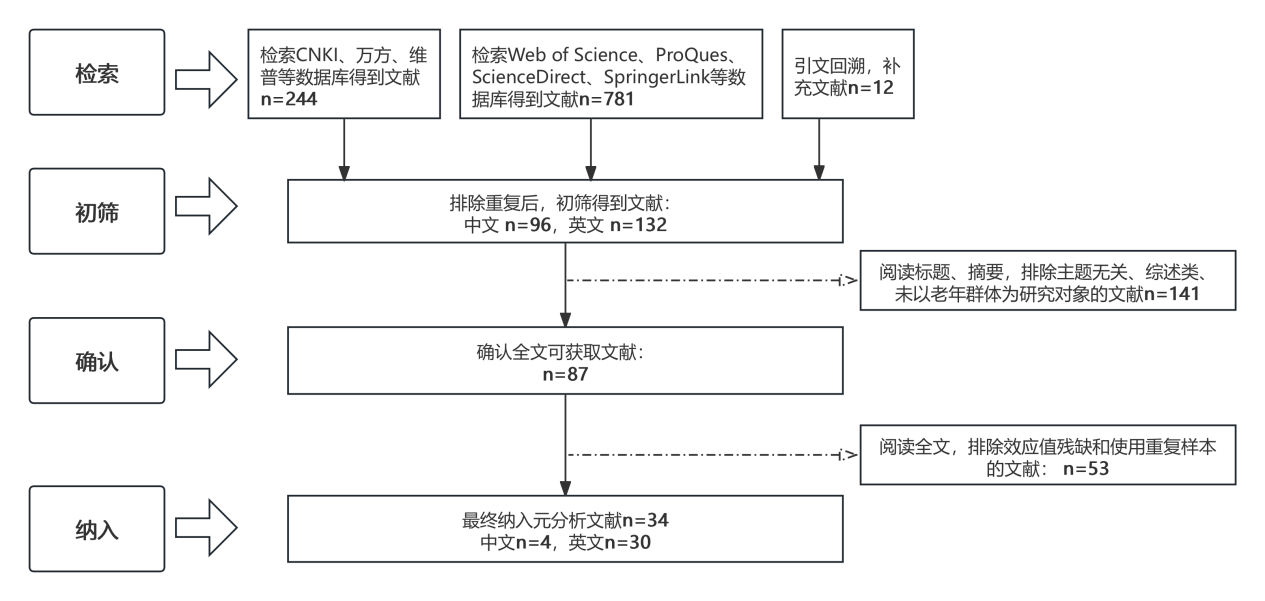
[目的/意义] 研究为理解和预测老年人的技术持续使用意愿提供有价值的参考依据,有助于指导智慧养老技术设计与改进,并进一步提升用户体验。 [方法/过程] 采用元分析方法,对34篇定量研究文献进行综合分析,着重探讨影响老年人智慧养老技术持续使用意愿的14组关键变量关系,并借助调节效应检验剖析研究结果的异质性来源。 [结果/结论] 研究结果显示,社会影响、便利条件、满意度、感知有用性、感知易用性、信任以及参与度与智慧养老技术持续使用意愿呈显著正相关关系。感知风险与技术焦虑则与持续使用意愿呈负相关关系。样本性别构成、所属国家经济发展水平、技术类别和样本规模可以调节变量间相关性,造成研究结果间的差异。
[Purpose/Significance] The study provides valuable references for understanding and predicting older adults’ smart senior technology continuance intention, which can help guide the design and improvement of smart senior technologies and further enhance the user experience. [Method/Process] The meta-analysis method was used to comprehensively analyze 34 quantitative research papers, focusing on the relationship between 14 groups of key variables that affect the intention of the elderly to continue to use smart senior technology, and the source of heterogeneity of the research results was analyzed with the help of the moderating effect test. [Result/Conclusion] The findings showed that social influence, facilitating condition, satisfaction, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, trust, and participation were significantly and positively related to smart senior technology continuance intention. In contrast, perceived risk and technology anxiety were negatively associated with smart senior technology continuance intention. In addition, the gender composition of the sample, the level of economic development of the country, the type of technology, and the size of the sample can moderate the correlations between the variables, resulting in differences between the findings.
older adults / smart senior technology / continuance intention / influencing factors / meta-analysis
| 1 |
中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.2023年我国卫生健康事业发展统计公报[EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/guihuaxxs/s3585u/202408/6c037610b3a54f6c8535c515844fae96/files/58c5d1e9876344e5b1aa5aa2b083a51a.pdf.
(The National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin on the Development of Health and Wellness Services in China in 2023 [EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. https://www.nhc.gov.cn/guihuaxxs/s3585u/202408/6c037610b3a54f6c8535c515844fae96/files/58c5d1e9876344e5b1aa5aa2b083a51a.pdf.)
|
| 2 |
中华人民共和国中央人民政府.习近平主持召开二十届中央财经委员会第一次会议[EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/2023-05/05/content_5754275.htm.
(The State Council of the People's Republic of China. Xi Jinping chairs the first meeting of the 20th Central Financial and Economic Affairs Commission [EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/2023-05/05/content_5754275.htm.)
|
| 3 |
北京市人民政府.北京市民政局等11部门关于印发《关于加强“老老人”服务保障的若干措施》的通知[EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. https://www.beijing.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengcefagui/202412/t20241204_3956319.html
(Beijing Municipal People's Government. Notice on the Issuance of Several Measures for Strengthening the Service and Guarantee for the Elderly Elderly by the Beijing Municipal Civil Affairs Bureau and Other 11 Departments [EB/OL]. [2025-03-07]. https://www.beijing.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengcefagui/202412/t20241204_3956319.html.)
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
刘勍勍, 左美云, 刘满成.基于期望确认理论的老年人互联网应用持续使用实证分析[J]. 管理评论, 2012, 24(5):89-101.
|
| 17 |
马琪, 杨薇, 廖舫仪.数字治理时代老年人数字融入困境形成机理研究[J]. 北大政治学评论, 2021(1):153-177.
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
郝瑞敏, 赵静, 闫东宁, 等.老年人持续使用康复机器人的动因研究与设计思考[J]. 包装工程, 2024, 45(16):16-29.
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
袁顺佳, 罗博, 张晋朝, 等.技术焦虑会阻碍老年人IT使用吗?[J]. 图书馆论坛, 2024, 44(2):103-113.
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
李华锋, 张瑞琦, 段加乐.基于元分析的在线持续知识共享意愿影响因素研究[J]. 情报科学, 2023, 41(1):49-60.
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
|
| 50 |
|
| 51 |
马琪, 陈浩鑫.智慧养老技术接受与政策助推路径初探——基于2005—2020年国内外文献的系统性整合分析[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2021(4):161-170.
|
| 52 |
|
| 53 |
|
| 54 |
|
| 55 |
王海晶.我国智慧养老服务的用户持续使用意愿及优化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2021.
|
| 56 |
|
| 57 |
|
| 58 |
|
杨 静:进行数据收集,撰写与修改论文;
马 琪:确定论文选题与框架,修改论文。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |