 PDF(1298 KB)
PDF(1298 KB)


 PDF(1298 KB)
PDF(1298 KB)
 PDF(1298 KB)
PDF(1298 KB)
在线评论与消费者退货意向:认知失调的多重中介效应分析
Online Reviews and Consumer Return Intention: Multiple Mediating Effects of Cognitive Dissonance
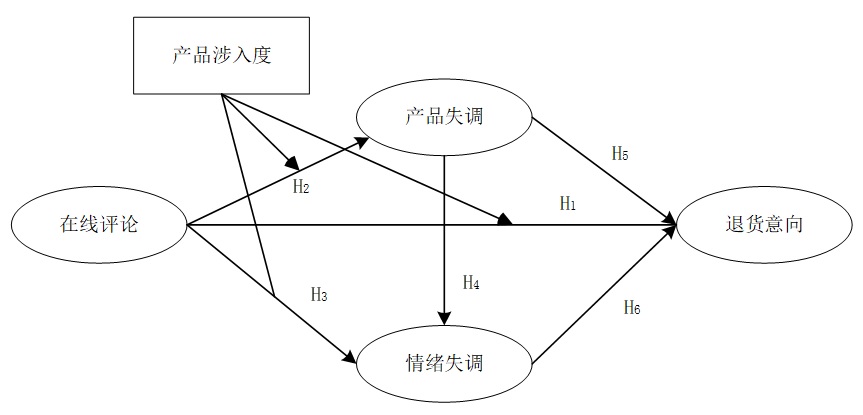
[目的/意义] 在线评论是消费者决策的重要参考依据,不仅可以提高产品的销售量,而且可以降低退货率。探索在线评论和消费者退货意向之间的关系,有助于进一步挖掘在线评论的价值。[方法/过程] 本研究运用SOR(刺激-机体-反应)和认知失调理论,构建消费者退货意向的概念模型。采用结构方程和Bootstrap中介检验以及调节检验,探讨在线评论对消费者退货意向的作用机制,并检验认知失调的多重中介作用及产品涉入度的调节效应。[结果/结论] 研究表明:较少的、低质量或低可信的在线评论通过产品失调和情绪失调正向影响退货意向,且情绪失调的中介效应大于产品失调的中介效应,产品失调和情绪失调的总中介效应大于在线评论对退货意向的直接效应,而产品涉入度对中介路径没有显著的调节作用。
[Purpose/significance] Online reviews play an important role on decision-making for consumers, which not only boost sales but also reduce the probability of product returns. Exploring the effect of online reviews on consumers' return intention will help to find the value of online reviews. [Method/process] In this paper, a conceptual model between online reviews and consumers' return intention was proposed based on SOR and cognitive dissonance theory. We explored the impact of online reviews on return intention using structural equation modeling and tested the multiple mediating effects of cognitive dissonance and moderating effects of product involvement by bootstrap. [Result/conclusion] The results show that the few, low quality or low reliability online reviews have significant positive effects on return intention. The emotion dissonance and product dissonance play a parallel and serial mediating role between online reviews and return intention, the mediating effect of emotion dissonance is greater than product dissonance does. But the product involvement has no significant moderating effect on mediation path.
在线评论 / SOR模型 / 认知失调 / 退货意向 / 产品涉入度
online reviews / SOR model / cognitive dissonance theory / return intention / product involvement
| [1] |
LEE D H. An alternative explanation of consumer product returns from the postpurchase dissonance and ecological marketing perspectives[J]. Psychology & marketing, 2015, 32(1):49-64.
|
| [2] |
CHEVALIER J A, MAYZLIN D. The effect of word of mouth on sales_ online book review[J]. Journal of marketing research, 2006, 43(3):345-354.
|
| [3] |
HU N, LIU L, ZHANG J. Do online reviews affect product sales? the role of reviewer characteristics and temporal effects[J]. Information technology & management, 2008, 9(3):201-214.
|
| [4] |
郝媛媛, 叶强, 李一军. 基于影评数据的在线评论有用性影响因素研究[J]. 管理科学学报, 2010, 13(8):78-88,96.
|
| [5] |
金立印. 网络口碑信息对消费者购买决策的影响:一个实验研究[J]. 经济管理, 2007(22):36-42.
|
| [6] |
SAHOO N, DELLAROCAS C, SRINIVASAN S. The impact of online product reviews on product returns[J]. Information systems research, 2018, 29(3):723-738.
|
| [7] |
KOTLER P. Atmospherics as a marketing tool[J]. Journal of retailing, 1974, 49(4):48-64.
|
| [8] |
MEHRABIAN A, RUSSELL J A. A verbal measure of information rate for studies in environmental psychology[J]. Environment and behavior, 1974, 6(2):233-252.
|
| [9] |
EROGLU S A, MACHLEITB K A, DAVISB L M. Atmospheric qualities of online retailing a conceptual model and implications[J]. Journal of business research, 2001, 54:177–184.
|
| [10] |
THANG D C L, TAN B L B. Linking consumer perception to preference of retail stores: an empirical assessment of the multi-attributes of store image[J]. Journal of retailing and consumer services, 2003, 10(4):193-200.
|
| [11] |
HSU H Y, TSOU H T. The effect of website quality on consumer emotional states and repurchases intention[J]. African journal of business management, 2011, 5(15):6195-6200.
|
| [12] |
KIM J Y, LENNON S J. Effects of reputation and website quality on online consumers' emotion, perceived risk and purchase intention: based on the stimulus-organism-response model[J]. Journal of research in interactive marketing, 2013, 7(1):33-56.
|
| [13] |
DONOVAN R J, ROSSITER J R, MARCOOLYN G, et al. Store atmosphere and purchasing behavior[J]. Journal of retailing, 1994, 70(3):283-29.
|
| [14] |
MICHON R, CHEBAT J C, TURLEY L W. Mall atmospherics: the interaction effects of the mall environment on shopping behavior[J]. Journal of business research, 2005, 58(5):576-583.
|
| [15] |
HARMON-JONES E, HARMON-JONES C. Cognitive dissonance theory after 50 years of development[J]. Zeitschrift für sozialpsychologie, 2007, 38(1):7-16.
|
| [16] |
MAO W, OPPEWAL H. Did I choose the right university? how post-purchase information affects cognitive dissonance, satisfaction and perceived service quality[J]. Australasian marketing journal, 2010, 18(1):28-35.
|
| [17] |
KIM Y S. Application of the cognitive dissonance theory to the service industry[J]. Services marketing quarterly, 2011, 32(2):96-112.
|
| [18] |
SWEENEY J C, HAUSKNECHT D, SOUTAR G N. Cognitive dissonance after purchase a multidimensional scale[J]. Psychology & marketing, 2000, 17(5):369-385.
|
| [19] |
SENECAL S, NANTEL J. The influence of online product recommendations on consumers’ online choices[J]. Journal of retailing, 2004, 80(2):159-169.
|
| [20] |
郑小平. 在线评论对网络消费者购买决策影响的实证研究[D]. 北京:中国人民大学, 2008.
|
| [21] |
龚诗阳, 刘霞, 赵平. 线上消费者评论如何影响产品销量?——基于在线图书评论的实证研究[J]. 中国软科学, 2013(6):171-183.
|
| [22] |
CHEN P Y, WU S Y, YOON J S. The impact of online recommendations and consumer feedback on sales[C]// Proceedings of the international conference on information systems. Seattle: Association for Information Systems, 2004:711-724.
|
| [23] |
PARK D H, LEE J, HAN I. The effect of on-line consumer reviews on consumer purchasing intention: the moderating role of involvement[J]. International journal of electronic commerce, 2007, 11(4):125-148.
|
| [24] |
魏华, 高劲松, 万辉. 电子商务平台消费者绿色产品评论信息采纳意愿研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(5):161-168.
|
| [25] |
朱丽叶, 袁登华, 张静宜. 在线用户评论质量与评论者等级对消费者购买意愿的影响——产品卷入度的调节作用[J]. 管理评论, 2017, 29(2):87-96.
|
| [26] |
冯娇, 姚忠. 基于社会学习理论的在线评论信息对购买决策的影响研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2016, 24(9):106-114.
|
| [27] |
MINNEMA A, BIJMOLT T H A, GENSLER S, et al. To keep or not to keep: effects of online customer reviews on product returns[J]. Journal of retailing, 2016, 92(3):253-267.
|
| [28] |
CHEUNG M Y, LUO C, SIA C L, et al. Credibility of electronic word-of-mouth: informational and normative determinants of on-line consumer recommendations[J]. International journal of electronic commerce, 2009, 13(4):9-38.
|
| [29] |
LAZARUS R S. Cognition and motivation in emotion[J]. American psychologist, 1991, 46(4):352-367.
|
| [30] |
CHEBAT J C, MICHON R. Impact of ambient odors on mall shoppers' emotions, cognition, and spending[J]. Journal of business research, 2003, 56(7):529-539.
|
| [31] |
POWERS T L, JACK E P. The influence of cognitive dissonance on retail product returns[J]. Psychology & marketing, 2013, 30(8):724-735.
|
| [32] |
ELLIOT A J, DEVINE P G. On the motivational nature of cognitive dissonance[J]. Journal of personality and social psychology, 1994, 67(3):382-394.
|
| [33] |
BREHM J W. Postdecision changes in the desirability of alternatives[J]. Journal of abnormal psychology, 1956, 52:384-389.
|
| [34] |
HONG Y K, PAVLOU P A. Product fit uncertainty in online markets[J]. Information systems research, 2014, 25(2):328-344.
|
| [35] |
ZAICHKOWSKY J L. The personal involvement inventory reduction[J]. Journal of advertising, 1994, 23(4):59-70.
|
| [36] |
方杰, 温忠麟, 张敏强,等. 基于结构方程模型的多重中介效应分析[J]. 心理科学, 2014, 37(3):735-741.
|
| [37] |
温忠麟, 叶宝娟. 有调节的中介模型检验方法:竞争还是替补?[J]. 心理学报, 2014, 46(5):714-726.
|
| [38] |
TAN Y C, GAN C C. The role of post-purchase emotional dissonance on product return intentions[J]. Global journal of business and social science review, 2014, 2(1):89-98.
|
| [39] |
ANDERSON E T, HANSEN K, SIMESTER D. The option value of returns: theory and empirical evidence[J]. Marketing science, 2009, 28(3):405-423.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |