 PDF(1532 KB)
PDF(1532 KB)


 PDF(1532 KB)
PDF(1532 KB)
 PDF(1532 KB)
PDF(1532 KB)
多任务环境下融合迁移学习的新冠疫情新闻要素识别研究
Research on Identification of COVID-19 News Elements based on Transfer Learning in Multi-task Environment
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,

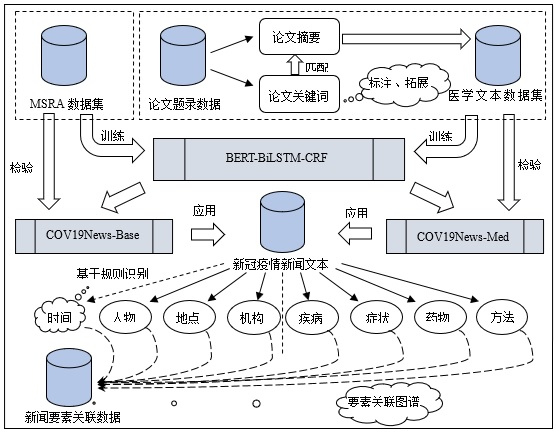
[目的/意义] 在新冠疫情背景下,提出多任务环境下融合迁移学习的疫情新闻要素识别方法,向公众提供面向应急事件的知识服务。[方法/过程] 首先,通过多任务识别新闻要素:基于规则识别时间要素;并融合模型迁移与深度学习方法,构建跨领域的要素识别模型。在此基础上,构建疫情新闻要素的关联数据,以知识图谱的方式展示各要素之间的关联关系。[结果/结论] 实验结果表明,除药物外的新闻要素的识别F1值均在80%以上,说明融合迁移学习的模型能够取得较优的识别效果;并且,关联数据知识图谱能够直观显示新闻的重点要素及新闻的主要内容。综上所述,提出的方法能够有效识别新冠疫情新闻要素,从而帮助新闻读者准确、高效地获取新闻中的重要信息。
[Purpose/significance] Under the background of novel coronavirus pneumonia, this paper proposes a method of identifying COVID-19 news elements in multi-task environment based on transfer learning to provide knowledge services of emergency for the public. [Method/process] Firstly, multiple tasks were used to identify news elements: Time elements were identified based on rules; besides, a cross domain element recognition model was constructed by integrating model transfer and deep learning methods. On this basis, the associated data of COVID-19 news elements was constructed, and the relationship between the elements was displayed by knowledge mapping. [Result/conclusion] The experimental results show that the F1 values of news elements except Drug are above 80%, which indicates that the transfer learning model can achieve fine recognition effect. Moreover, the knowledge map of associated data can intuitively display the key elements and main contents of news. In conclusion, the method proposed in this paper can effectively identify elements in COVID-19 news, thus it can help readers obtain important information from the news accurately and efficiently.
多任务 / 迁移学习 / 新冠 / 新闻要素识别 / 命名实体识别 / 冷启动
multi-task / transfer learning / COVID-19 / news elements identification / named entity recognition / cold start
| [1] |
王岩, 蒿兴华, 薛鹏. 基于共词分析和社会网络分析的关联数据知识图谱构建分析[J]. 数字通信世界, 2020(6):148-150.
|
| [2] |
陶洁. 基于新闻文本的关键词提取[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2019.
|
| [3] |
陶天一, 王清钦, 付聿炜, 等. 基于知识图谱的金融新闻个性化推荐算法[J/OL]. 计算机工程, 2020: 1-10 [2020-09-12]. https://doi.org/10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0057446.
|
| [4] |
裴韬, 郭思慧, 袁烨城, 等. 面向公共安全事件的网络文本大数据结构化研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(1):2-13.
|
| [5] |
吉雷静. 面向网页文本的地理信息变化语义检测方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2013.
|
| [6] |
伏恺. Web新闻文本信息抽取与可视化研究[D]. 济南: 山东财经大学, 2017.
|
| [7] |
KRSTEV C, OBRADOVIC I, UTVIC M, et al. A system for named entity recognition based on local grammars[J]. Journal of logic and computation, 2014, 24(2):473-489.
|
| [8] |
杨建林, 王文龙. 公共卫生类突发事件的抽取研究[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2016, 39(4) :51-59.
|
| [9] |
KUCUK D, YAZICI A. A hybrid named entity recognizer for Turkish[J]. Expert systems with applications, 2012, 39(3):2733-2742.
|
| [10] |
SEKER G A, ERYIGIT G. Extending a CRF-based named entity recognition model for Turkish well formed text and user generated content[J]. Semantic Web, 2017, 8(5):625-642.
|
| [11] |
吴伟成. 基于恐怖袭击事件语料库的时间短语抽取研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016.
|
| [12] |
CHASIN R, WOODWARD D, WITMER J, et al. Extracting and displaying temporal and geospatial entities from articles on historical events[J]. Computer journal, 2014,57(3):403-426.
|
| [13] |
李玉超. 新闻事件地名实体识别和地图链接技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.
|
| [14] |
WICHMANN P, BRINTRUP A, BAKER S, et al. Extracting supply chain maps from news articles using deep neural networks[J]. International journal of production research, 2020, 58(17):5320-5336.
|
| [15] |
XU J G, GUO L X, JIANG J, et al. A deep learning methodology for automatic extraction and discovery of technical intelligence[J]. Technological forecasting and social change, 2019, 146 :339-351.
|
| [16] |
王昊, 邓三鸿, 朱立平, 等. 大数据环境下政务数据的情报价值及其利用研究——以海关报关商品归类风险规避为例[J]. 科技情报研究, 2020, 2(4):74-89.
|
| [17] |
DONG X S, CHOWDHURY S, QIAN L J, et al. Deep learning for named entity recognition on Chinese electronic medical records: combining deep transfer learning with multitask bi-directional LSTM RNN[J]. PLOS one, 2019, 14(5):1-15.
|
| [18] |
肖连杰, 孟涛, 王伟, 等. 基于深度学习的情报分析方法识别研究——以安全情报领域为例[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2019, 3(10):20-28.
|
| [19] |
DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[EB/OL].[2020-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805.
|
| [20] |
李灵芳, 杨佳琦, 李宝山, 等. 基于BERT的中文电子病历命名实体识别[J]. 内蒙古科技大学学报, 2020, 39(1):71-77.
|
| [21] |
吴俊, 程垚, 郝瀚, 等. 基于BERT嵌入BiLSTM-CRF模型的中文专业术语抽取研究[J]. 情报学报, 2020, 39(4):409-418.
|
| [22] |
刘忠宝, 党建飞, 张志剑.《史记》历史事件自动抽取与事理图谱构建研究[J]. 图书情报工作, 2020, 64(11):116-124.
|
| [23] |
YOSINSKI J, CLUNE J, BENGIO Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? [EB/OL]. [2020-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1792.
|
| [24] |
陈美杉, 夏晨曦. 肝癌患者在线提问的命名实体识别研究:一种基于迁移学习的方法[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2019, 3(12):61-69.
|
| [25] |
李号号. 基于实例的迁移学习技术研究及应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018.
|
| [26] |
陈文珺, 杨佳佳. 基于共享知识迁移学习的跨领域推荐研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(6):126-132.
|
| [27] |
GLIGIC L, KORMILITZIN A, GOLDBERG P, et al. Named entity recognition in electronic health records using transfer learning bootstrapped neural networks[J]. Neural networks, 2020, 121 :132-139.
|
| [28] |
KUNG H K, HSIEH C M, HO C Y, et al. Data-augmented hybrid named entity recognition for disaster management by transfer learning[J]. Applied sciences-basel, 2020, 10(12):1-17.
|
| [29] |
邵明锐, 马登豪, 陈跃国, 等. 基于社区问答数据迁移学习的FAQ问答模型研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019(5):74-84.
|
| [30] |
Al-SMADI M, Al-ZBOON S, JARARWEH Y, et al. Transfer learning for Arabic named entity recognition with deep neural networks[J]. IEEE access, 2020,8:37736-37745.
|
| [31] |
刘宇飞, 尹力, 张凯, 等. 基于深度迁移学习的技术术语识别——以数控系统领域为例[J]. 情报杂志, 2019, 38(10):168-175.
|
| [32] |
孔祥鹏, 吾守尔·斯拉木, 杨启萌, 等. 基于迁移学习的维吾尔语命名实体识别[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 2020, 52(2):58-65.
|
| [33] |
站长之家. 新闻媒体网站排行榜[EB/OL]. [2020-09-30]. https://top.chinaz.com/hangye/index_news.html.
|
| [34] |
李飞, 朱艳辉, 王天吉, 等. 基于医疗类别的电子病历命名实体识别研究[J]. 湖南工业大学学报, 2018, 32(4):61-66.
|
| [35] |
赵青, 王丹, 徐书世, 等. 一种基于RNN的弱监督中文医疗实体识别方法[J/OL]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020:1-10[2020-09-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1390.U.20200330.1522.002.html.
|
| [36] |
夏光辉, 李军莲, 邢宝坤, 等. 基于中文病例报告文献的医学诊疗命名实体识别研究[J]. 医学信息学杂志, 2019, 40(6):54-59.
|
| [37] |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[EB/OL]. [2020-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762.
|
赵梓博: 负责完成实验,撰写论文初稿;
王昊: 指导研究思路,核查论文内容并提出修改意见;
刘友华: 负责整理实验结果,审查异常数据指标并提出改进策略;
张卫: 提供有关可视化方法、工具的指导建议,并参与修改终稿;
孟镇: 负责修改终稿。
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |