 PDF(1815 KB)
PDF(1815 KB)


 PDF(1815 KB)
PDF(1815 KB)
 PDF(1815 KB)
PDF(1815 KB)
知识密集型服务业与制造业协同集聚的创新效应研究
Innovation Effect of Co-agglomeration Between KIBS and Manufacturing Industry
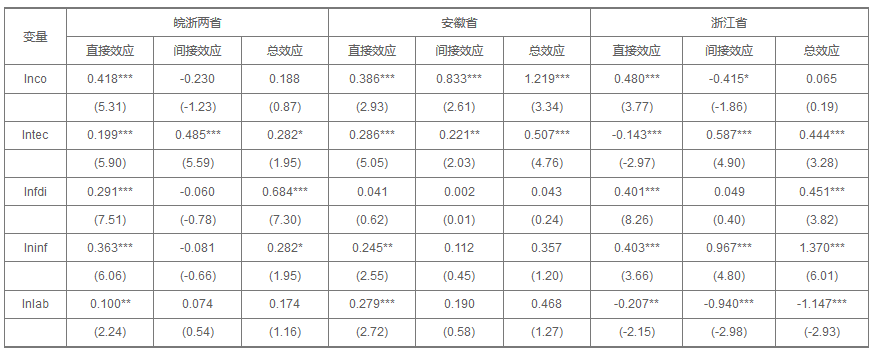
[目的/意义] 旨在比较分析知识密集型服务业与制造业在不同发展阶段和不同的区域协同集聚的创新效应。[方法/过程] 在理论分析的基础上,以安徽省和浙江省27个城市为研究对象,选取2003-2015年的面板数据,运用空间计量回归模型分析和比较两个省份知识密集型服务业与制造业的产业协同集聚度对创新产出的影响情况。[结果/结论] 知识密集型服务业与制造业的协同集聚能够形成区域创新群落,带动整个区域的创新发展,但是从具体情况来看,存在高水平城市对低水平城市的极化效应,其中浙江省的极化效应更加明显,这不利于区域整体的均衡全面发展,需要上级政府的正确引导和下级政府的积极配合加以改善。
[Purpose/significance] This paper aims at comparing and analyzing the innovative effects on collaborative concentration of knowledge-intensive busines service industry(KIBS)and manufacturing industries at different development stages in different regions. [Method/process] On the basis of theoretical analysis, the paper took 27 cities in Anhui Province and Zhejiang Province as the research objects, selected the panel data from 2003 to 2014, analyzed and compared the impact of co-agglomeration between KIBS and manufacturing industry on regional innovation capacity of the two provinces by using the spatial regression model. [Result/conclusion] The co-agglomeration between KIBS and manufacturing industry can form regional innovation community, it can promote the innovation and development of the whole region. However, from the specific situation, high-level cities will have polarization effect on low-level especially in Zhejiang province. This phenomenon is not conducive to the overall development of the regional, it requires the correct guidance of superior governments and the active cooperation of grass-roots governments.
knowledge-intensive business service / manufacturing industry / collaborative agglomeration / spatial econometric
| [1] |
王国顺, 张凡, 郑准. 我国知识密集型服务业的空间集聚水平及影响因素——基于288个城市数据的实证研究[J]. 经济地理, 2016, 36(4):106-112.
|
| [2] |
刘洋. 我国知识密集型服务业影响区域创新效率的实证研究[D].长沙:湖南大学, 2014.
|
| [3] |
魏江, 陶颜, 王琳. 知识密集型服务业的概念与分类研究[J]. 中国软科学, 2007(1):33-41.
|
| [4] |
CIRIACI D. MONTRESOR S. PALMA D. Do KIBS make manufacturing more innovative? an empirical investigation of four European countries [J]. Technological forecasting and social change,2014,95(1):131-151.
|
| [5] |
陈建军, 刘月, 邹苗苗. 产业协同集聚下的城市生产效率增进——基于融合创新与发展动力转换背景[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2016(3):150-163.
|
| [6] |
时省, 赵定涛, 洪进.集聚视角下知识密集型服务业对区域创新的影响研究[J]. 科学学与科学技术管理, 2013(12):167-174.
|
| [7] |
李向东, 李南, 白俊红. 高技术产业研发创新效率分析[J]. 中国软科学, 2011(2):52-61.
|
| [8] |
吕民乐, 金妍. 知识密集型服务业对中国制造业创新的影响——基于高技术制造业的实证分析[J]. 工业技术经济, 2016, 35(4):17-24.
|
| [9] |
张振刚, 李云健, 陈志明. 科技服务业对区域创新能力提升的影响——基于珠三角地区的实证研究[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2013, 1(12):45-51.
|
| [10] |
ELLISON G, GLAESER E L. Geographic concentration in U.S. manufacturing industries: a dartboard approach[J]. Journal of political economy, 1997, 105(5):889-927.
|
| [11] |
DURANTON G, OVERMAN H G. Testing for localization using micro-geographic data[J]. Review of economic studies, 2005, 72(4):1077-1106.
|
| [12] |
BILLINGS S B, JOHNSON E B. Agglomeration within an urban area[J]. Journal of urban economics, 2016, 91(1):13-25.
|
| [13] |
陈国亮, 陈建军. 产业关联、空间地理与二三产业共同集聚——来自中国212个城市的经验考察[J]. 管理世界, 2012(4):82-100.
|
| [14] |
杨仁发. 产业集聚与地区工资差距——基于我国269个城市的实证研究[J]. 管理世界, 2013(8):41-52.
|
| [15] |
杜传忠, 王鑫, 刘忠京. 制造业与生产性服务业耦合协同能提高经济圈竞争力吗?——基于京津冀与长三角两大经济圈的比较[J]. 产业经济研究, 2013(6): 19-28.
|
| [16] |
豆建民, 刘叶. 生产性服务业与制造业协同集聚是否能促进经济增长——基于中国285个地级市的面板数据[J]. 现代财经-天津财经大学学报, 2016(4):92-102.
|
| [17] |
树友林, 王怀民. 地区信息化水平与经济增长内生性关系研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2007, 26(10):85-86.
|
| [18] |
李雷鸣, 贾江涛. 信息化与能源效率的关系研究[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(5):163-166.
|
| [19] |
GONZÁLEZ-LOUREIRO M, PITA-CASTELO J. A model for assessing the contribution of innovative smes to economic growth: the intangible approach[J]. Economics letters, 2012, 116(3):312–315.
|
| [20] |
林毅夫, 孙希芳. 银行业结构与经济增长[J]. 经济研究, 2008(9):31-45.
|
| [21] |
廖敬文. 长江中游城市群产业结构升级的空间溢出效应[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2016, 30(8):32-39.
|
| [22] |
李习保. 区域创新环境对创新活动效率影响的实证研究[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2007, 24(8):13-24.
|
| [23] |
ANSELIN L, LE GALLO J, JAYET H. Spatial panel econometrics[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2008: 625-660.
|
| [24] |
ELHORST J P. Dynamic spatial panels: models, methods, and inferences[J]. Journal of geographical systems, 2012, 14(1):5-28.
|
| [25] |
陈强.高级计量经济学及Stata应用[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2014:593-594.
|
| [26] |
金刚, 沈坤荣, 胡汉辉. 中国省际创新知识的空间溢出效应测度——基于地理距离的视角[J]. 经济理论与经济管理, 2015, 35(12):30-43.
|
| [27] |
张璐璐.知识产权保护、市场化对产业集聚的影响研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2013.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |